Neurotrophic Factors in Experimental Cerebral Acanthamoebiasis
- PMID: 35563321
- PMCID: PMC9103668
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23094931
Neurotrophic Factors in Experimental Cerebral Acanthamoebiasis
Abstract
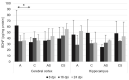
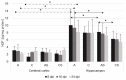
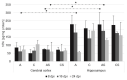
To date, no studies have addressed the role of neurotrophins (NTs) in Acanthamoeba spp. infections in the brain. Thus, to clarify the role of NTs in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus during experimental acanthamoebiasis in relation to the host immune status, the purpose of this study was to determine whether Acanthamoeba spp. may affect the concentration of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), nerve growth factor (NGF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), and neurotrophin-4 (NT-4) in brain structures. Our results suggest that at the beginning of infection in immunocompetent hosts, BDNF and NT-3 may reflect an endogenous attempt at neuroprotection against Acanthamoeba spp. infection. We also observed a pro-inflammatory effect of NGF during acanthamoebiasis in immunosuppressed hosts. This may provide important information for understanding the development of cerebral acanthamoebiasis related to the immunological status of the host. However, the pathogenesis of brain acanthamoebiasis is still poorly understood and documented and, therefore, requires further research.
Keywords: Acanthamoeba spp.; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; cerebral cortex; hippocampus; immunological status; nerve growth factor; neurotrophin-3; neurotrophin-4.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immunohistochemical distribution of NGF, BDNF, NT-3, and NT-4 in adult rhesus monkey brains.J Histochem Cytochem. 2007 Jan;55(1):1-19. doi: 10.1369/jhc.6A6952.2006. Epub 2006 Aug 9. J Histochem Cytochem. 2007. PMID: 16899765
-
Age-dependent time course of cerebral brain-derived neurotrophic factor, nerve growth factor, and neurotrophin-3 in APP23 transgenic mice.J Neurosci Res. 2008 Sep;86(12):2774-83. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21704. J Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18438945
-
Region-specific neurotrophin imbalances in Alzheimer disease: decreased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and increased levels of nerve growth factor in hippocampus and cortical areas.Arch Neurol. 2000 Jun;57(6):846-51. doi: 10.1001/archneur.57.6.846. Arch Neurol. 2000. PMID: 10867782
-
Neurotrophins and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in the ovary: physiological and pathophysiological implications.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 Mar 1;25(2):224-242. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmy047. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 30608586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nerve growth factor in the psychiatric brain.Riv Psichiatr. 2020 Jan-Feb;55(1):4-15. doi: 10.1708/3301.32713. Riv Psichiatr. 2020. PMID: 32051620 Review.
Cited by
-
Macroelement and Microelement Levels in the Urine in Experimental Acanthamoebiasis.Pathogens. 2023 Aug 14;12(8):1039. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12081039. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37623999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Łanocha-Arendarczyk N., Baranowska-Bosiacka I., Gutowska I., Kolasa-Wołosiuk A., Kot K., Łanocha A., Metryka E., Wiszniewska B., Chlubek D., Kosik-Bogacka D. The activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-9) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMP-1, TIMP-3) in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus in experimental acanthamoebiasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018;19:4128. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124128. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

