Imbalance in Sirt1 Alternative Splicing in Response to Chronic Stress during the Adolescence Period in Female Mice
- PMID: 35563336
- PMCID: PMC9104080
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23094945
Imbalance in Sirt1 Alternative Splicing in Response to Chronic Stress during the Adolescence Period in Female Mice
Abstract
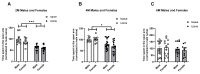
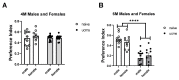
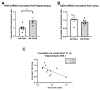
Stressful unpredictable life events have been implicated in numerous diseases. It is now becoming clear that some life periods are more vulnerable than others. As adolescence is a sensitive period in brain development, the long-term effects of stress during this period could be significant. We investigated the long-term effects of exposure to unpredictable chronic mild stress in adolescent mice on alternative splicing of Sirtuin 1. One-month-old mice were exposed to 4 weeks of UCMS and examined for anxiety and cognition at the age of 2, 4 and 6 months. We found a rise in anxious behavior immediately after the exposure to stress. Notably, there was a long-term impairment of performance in cognitive tasks and an imbalance in Sirtuin 1 and TrkB receptor alternative splicing in the stress-exposed mice compared with controls. To conclude, our results show that exposure to unpredictable chronic mild stress during adolescence affects cognition in adulthood. Understanding pathways affiliated with stress may help minimize the long-term emotional effects of an unpredictable, stressful event.
Keywords: Sirt1; TrkB; cognition; senescence; unpredictable stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Baglietto-Vargas D., Chen Y., Suh D., Ager R.R., Rodriguez-Ortiz C.J., Medeiros R., Myczek K., Green K.N., Baram T.Z., LaFerla F.M. Short-Term Modern Life-like Stress Exacerbates Aβ-Pathology and Synapse Loss in 3xTg-AD Mice. J. Neurochem. 2015;134:915–926. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13195. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

