Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease in the Current State: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 35563350
- PMCID: PMC9102515
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23094962
Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease in the Current State: A Narrative Review
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) has become a problem, owing to its high prevalence in an aging society with no treatment available after onset. However, early diagnosis is essential for preventive intervention to delay disease onset due to its slow progression. The current AD diagnostic methods are typically invasive and expensive, limiting their potential for widespread use. Thus, the development of biomarkers in available biofluids, such as blood, urine, and saliva, which enables low or non-invasive, reasonable, and objective evaluation of AD status, is an urgent task. Here, we reviewed studies that examined biomarker candidates for the early detection of AD. Some of the candidates showed potential biomarkers, but further validation studies are needed. We also reviewed studies for non-invasive biomarkers of AD. Given the complexity of the AD continuum, multiple biomarkers with machine-learning-classification methods have been recently used to enhance diagnostic accuracy and characterize individual AD phenotypes. Artificial intelligence and new body fluid-based biomarkers, in combination with other risk factors, will provide a novel solution that may revolutionize the early diagnosis of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease (AD); biomarkers; low or non-invasively; machine-learning classification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
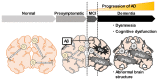

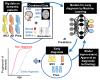
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Action Plan on the Public Health Response to Dementia 2017–2025. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

