Urine-Derived Stem Cell-Secreted Klotho Plays a Crucial Role in the HK-2 Fibrosis Model by Inhibiting the TGF-β Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 35563402
- PMCID: PMC9105028
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23095012
Urine-Derived Stem Cell-Secreted Klotho Plays a Crucial Role in the HK-2 Fibrosis Model by Inhibiting the TGF-β Signaling Pathway
Abstract
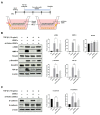
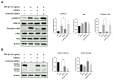
Renal fibrosis is an irreversible and progressive process that causes severe dysfunction in chronic kidney disease (CKD). The progression of CKD stages is highly associated with a gradual reduction in serum Klotho levels. We focused on Klotho protein as a key therapeutic factor against CKD. Urine-derived stem cells (UDSCs) have been identified as a novel stem cell source for kidney regeneration and CKD treatment because of their kidney tissue-specific origin. However, the relationship between UDSCs and Klotho in the kidneys is not yet known. In this study, we discovered that UDSCs were stem cells that expressed Klotho protein more strongly than other mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). UDSCs also suppressed fibrosis by inhibiting transforming growth factor (TGF)-β in HK-2 human renal proximal tubule cells in an in vitro model. Klotho siRNA silencing reduced the TGF-inhibiting ability of UDSCs. Here, we suggest an alternative cell source that can overcome the limitations of MSCs through the synergetic effect of the origin specificity of UDSCs and the anti-fibrotic effect of Klotho.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; klotho; mesenchymal stem cells; renal fibrosis; urine-derived stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that no support, financial or otherwise, has been received from any organization that may have an interest in the submitted work and there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work. EHLBIO Co., LTD. had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Kusek J.W., Greene P., Wang S.R., Beck G., West D., Jamerson K., Agodoa L.Y., Faulkner M., Level B. Cross-sectional study of health-related quality of life in African Americans with chronic renal insufficiency: The African American Study of Kidney Disease and Hypertension Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002;39:513–524. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2002.31401. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

