Metabolism and DNA Adduct Formation of Tobacco-Specific N-Nitrosamines
- PMID: 35563500
- PMCID: PMC9104174
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23095109
Metabolism and DNA Adduct Formation of Tobacco-Specific N-Nitrosamines
Abstract
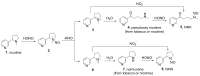
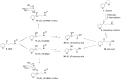
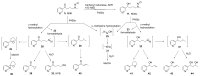
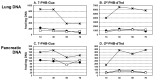
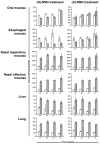
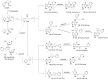
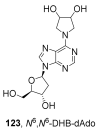
The tobacco-specific N-nitrosamines 4-(N-nitrosomethylamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) and N'-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) always occur together and exclusively in tobacco products or in environments contaminated by tobacco smoke. They have been classified as "carcinogenic to humans" by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. In 1998, we published a review of the biochemistry, biology and carcinogenicity of tobacco-specific nitrosamines. Over the past 20 years, considerable progress has been made in our understanding of the mechanisms of metabolism and DNA adduct formation by these two important carcinogens, along with progress on their carcinogenicity and mutagenicity. In this review, we aim to provide an update on the carcinogenicity and mechanisms of the metabolism and DNA interactions of NNK and NNN.
Keywords: DNA adducts; NNK; NNN; metabolism; tobacco-specific N-nitrosamines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



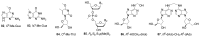
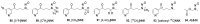

References
-
- Islami F., Goding Sauer A., Miller K.D., Siegel R.L., Fedewa S.A., Jacobs E.J., McCullough M.L., Patel A.V., Ma J., Soerjomataram I., et al. Proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to potentially modifiable risk factors in the United States. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:31–54. doi: 10.3322/caac.21440. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

