Continuous Ingestion of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus JB-1 during Chronic Stress Ensures Neurometabolic and Behavioural Stability in Rats
- PMID: 35563564
- PMCID: PMC9106030
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23095173
Continuous Ingestion of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus JB-1 during Chronic Stress Ensures Neurometabolic and Behavioural Stability in Rats
Abstract
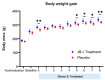
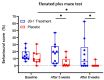
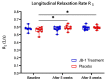
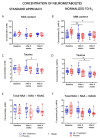
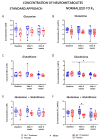
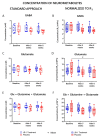
The intestinal microbiome composition and dietary supplementation with psychobiotics can result in neurochemical alterations in the brain, which are possible due to the presence of the brain-gut-microbiome axis. In the present study, magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) and behavioural testing were used to evaluate whether treatment with Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus JB-1 (JB‑1) bacteria alters brain metabolites' levels and behaviour during continuous exposure to chronic stress. Twenty Wistar rats were subjected to eight weeks of a chronic unpredictable mild stress protocol. Simultaneously, half of them were fed with JB-1 bacteria, and the second half was given a daily placebo. Animals were examined at three-time points: before starting the stress protocol and after five and eight weeks of stress onset. In the elevated plus maze behavioural test the placebo group displayed increased anxiety expressed by almost complete avoidance of exploration, while the JB-1 dietary supplementation mitigated anxiety which resulted in a longer exploration time. Hippocampal MRS measurements demonstrated a significant decrease in glutamine + glutathione concentration in the placebo group compared to the JB-1 bacteria-supplemented group after five weeks of stress. With the progression of stress the decrease of glutamate, glutathione, taurine, and macromolecular concentrations were observed in the placebo group as compared to baseline. The level of brain metabolites in the JB-1-supplemented rats were stable throughout the experiment, with only the taurine level decreasing between weeks five and eight of stress. These data indicated that the JB-1 bacteria diet might stabilize levels of stress-related neurometabolites in rat brain and could prevent the development of anxiety/depressive-like behaviour.
Keywords: Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus JB-1; brain–gut–microbiome axis; chronic unpredictable mild stress; depression; magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Mittal R., Debs L.H., Patel A.P., Nguyen D., Patel K., O’Connor G., Grati M., Mittal J., Yan D., Eshraghi A.A., et al. Neurotransmitters: The Critical Modulators Regulating Gut-Brain Axis: Role of Serotonin and Catecholamines in Gut/Brain Axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017;232:2359–2372. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25518. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

