AOM/DSS Induced Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer in 14-Month-Old Female Balb/C and C57/Bl6 Mice-A Pilot Study
- PMID: 35563665
- PMCID: PMC9104960
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23095278
AOM/DSS Induced Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer in 14-Month-Old Female Balb/C and C57/Bl6 Mice-A Pilot Study
Abstract
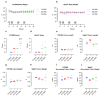
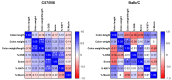
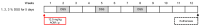
Colitis is a major risk factor for the development of colorectal cancer, leading to colitis-associated colorectal cancer (CAC). The most commonly used animal model to study CAC is the azoxymethane-dextran sulphate-sodium (AOM/DSS) model. The ideal experimental conditions of this model depend on several factors, including the used mouse strain. No data on feasibility and conditions for older mice, e.g., for aging studies, have yet been reported. Thus, we conducted a descriptive, observational pilot study where CAC was induced in 14-month-old female Balb/C and C57/Bl6 mice using 12.5 mg/kg AOM i.p. and three different concentrations of DSS (1, 2, and 3%) in drinking water (ad. lib.). The mice were monitored regularly during the three-month experimental phase. After euthanasia, the colons of the mice were evaluated macroscopically and microscopically. Both the mouse strains showed a DSS-concentration-dependent induction of CAC. Carcinomas were only observed at 3% DSS. The DSS dose was found to be significantly correlated with the histology score and % Ki67 positive cells only in C57/Bl6 mice but not in Balb/C mice, which showed a variable response to the CAC induction. No differences in colon length, weight, or mucin content were observed. Optimal conditions for CAC induction in these aged animals are thus considered to be 3% DSS, as carcinomas did not develop when 2% DSS was used. On the other hand, Balb/C mice reacted severely to 3% DSS, indicating that 2.5% DSS may be the "sweet spot" for future experiments comparing CAC in aged Balb/C and C57/Bl6 mice. This model will allow investigation of the effect of aging on CAC development and therapy.
Keywords: AOM; DSS; aged mice; colitis associated colorectal cancer; mouse strain differences; pilot study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Groschel C., Prinz-Wohlgenannt M., Mesteri I., Karuthedom George S., Trawnicek L., Heiden D., Aggarwal A., Tennakoon S., Baumgartner M., Gasche C., et al. Switching to a Healthy Diet Prevents the Detrimental Effects of Western Diet in a Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer Model. Nutrients. 2019;12:45. doi: 10.3390/nu12010045. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

