The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Metabolic Reprogramming of the Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 35563739
- PMCID: PMC9104192
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11091433
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Metabolic Reprogramming of the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
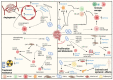
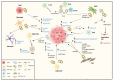
The tumor microenvironment (TME) includes a network of cancerous and non-cancerous cells, together with associated blood vessels, the extracellular matrix, and signaling molecules. The TME contributes to cancer progression during various phases of tumorigenesis, and interactions that take place within the TME have become targets of focus in cancer therapy development. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are known to be conveyors of genetic material, proteins, and lipids within the TME. One of the hallmarks of cancer is its ability to reprogram metabolism to sustain cell growth and proliferation in a stringent environment. In this review, we provide an overview of TME EV involvement in the metabolic reprogramming of cancer and stromal cells, which favors cancer progression by enhancing angiogenesis, proliferation, metastasis, treatment resistance, and immunoevasion. Targeting the communication mechanisms and systems utilized by TME-EVs is opening a new frontier in cancer therapy.
Keywords: cancer metabolism; exosomes; extracellular vesicles (EVs); glycolysis; tumor microenvironment (TME).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stincone A., Prigione A., Cramer T., Wamelink M.M.C., Campbell K., Cheung E., Olin-Sandoval V., Grüning N.-M., Krüger A., Tauqeer Alam M., et al. The return of metabolism: Biochemistry and physiology of the pentose phosphate pathway. Biol. Rev. 2015;90:927–963. doi: 10.1111/brv.12140. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

