How CAR T Cells Breathe
- PMID: 35563759
- PMCID: PMC9102061
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11091454
How CAR T Cells Breathe
Abstract
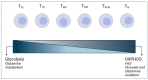
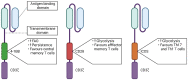
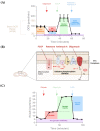
The manufacture of efficacious CAR T cells represents a major challenge in cellular therapy. An important aspect of their quality concerns energy production and consumption, known as metabolism. T cells tend to adopt diverse metabolic profiles depending on their differentiation state and their stimulation level. It is therefore expected that the introduction of a synthetic molecule such as CAR, activating endogenous signaling pathways, will affect metabolism. In addition, upon patient treatment, the tumor microenvironment might influence the CAR T cell metabolism by compromising the energy resources. The access to novel technology with higher throughput and reduced cost has led to an increased interest in studying metabolism. Indeed, methods to quantify glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration have been available for decades but were rarely applied in the context of CAR T cell therapy before the release of the Seahorse XF apparatus. The present review will focus on the use of this instrument in the context of studies describing the impact of CAR on T cell metabolism and the strategies to render of CAR T cells more metabolically fit.
Keywords: CAR; T cells; chimeric antigen receptor; metabolism; tonic signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Remodeling metabolic fitness: Strategies for improving the efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy.Cancer Lett. 2022 Mar 31;529:139-152. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.01.006. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35007698 Review.
-
A metabolic switch to memory CAR T cells: Implications for cancer treatment.Cancer Lett. 2021 Mar 1;500:107-118. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.12.004. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33290868
-
Disruption of adenosine 2A receptor improves the anti-tumor function of anti-mesothelin CAR T cells both in vitro and in vivo.Exp Cell Res. 2021 Dec 1;409(1):112886. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112886. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Exp Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 34673000
-
Adoptive Transfer of IL13Rα2-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells Creates a Pro-inflammatory Environment in Glioblastoma.Mol Ther. 2018 Apr 4;26(4):986-995. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Mol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29503195 Free PMC article.
-
Paving New Roads for CARs.Trends Cancer. 2019 Oct;5(10):583-592. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.09.005. Epub 2019 Oct 19. Trends Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31706506 Review.
Cited by
-
Determination of CAR T cell metabolism in an optimized protocol.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jun 20;11:1207576. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1207576. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37409169 Free PMC article.
-
Nondestructive, longitudinal, 3D oxygen imaging of cells in a multi-well plate using pulse electron paramagnetic resonance imaging.Npj Imaging. 2024 Apr 1;2(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s44303-024-00013-7. Npj Imaging. 2024. PMID: 40604125 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of chimeric antigen receptor T cell metabolism to improve therapeutic outcomes.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 14;14:1121565. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1121565. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36999013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

