Novel Therapeutic Approaches with DNA Damage Response Inhibitors for Melanoma Treatment
- PMID: 35563772
- PMCID: PMC9099918
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11091466
Novel Therapeutic Approaches with DNA Damage Response Inhibitors for Melanoma Treatment
Abstract
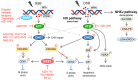
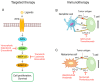
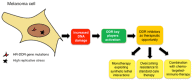
Targeted therapies against components of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and immunotherapies, which block immune checkpoints, have shown important clinical benefits in melanoma patients. However, most patients develop resistance, with consequent disease relapse. Therefore, there is a need to identify novel therapeutic approaches for patients who are resistant or do not respond to the current targeted and immune therapies. Melanoma is characterized by homologous recombination (HR) and DNA damage response (DDR) gene mutations and by high replicative stress, which increase the endogenous DNA damage, leading to the activation of DDR. In this review, we will discuss the current experimental evidence on how DDR can be exploited therapeutically in melanoma. Specifically, we will focus on PARP, ATM, CHK1, WEE1 and ATR inhibitors, for which preclinical data as single agents, taking advantage of synthetic lethal interactions, and in combination with chemo-targeted-immunotherapy, have been growing in melanoma, encouraging the ongoing clinical trials. The overviewed data are suggestive of considering DDR inhibitors as a valid therapeutic approach, which may positively impact the future of melanoma treatment.
Keywords: ATM; ATR; CHK1; DNA damage response; PARP; WEE1; combined therapy; inhibitors; melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

