Platelet Versus Megakaryocyte: Who Is the Real Bandleader of Thromboinflammation in Sepsis?
- PMID: 35563812
- PMCID: PMC9104300
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11091507
Platelet Versus Megakaryocyte: Who Is the Real Bandleader of Thromboinflammation in Sepsis?
Abstract
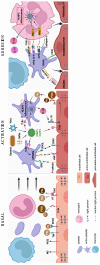
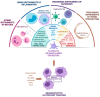
Platelets are mainly known for their key role in hemostasis and thrombosis. However, studies over the last two decades have shown their strong implication in mechanisms associated with inflammation, thrombosis, and the immune system in various neoplastic, inflammatory, autoimmune, and infectious diseases. During sepsis, platelets amplify the recruitment and activation of innate immune cells at the site of infection and contribute to the elimination of pathogens. In certain conditions, these mechanisms can lead to thromboinflammation resulting in severe organ dysfunction. Here, we discuss the interactions of platelets with leukocytes, neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), and endothelial cells during sepsis. The intrinsic properties of platelets that generate an inflammatory signal through the NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome are discussed. As an example of immunothrombosis, the implication of platelets in vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia is documented. Finally, we discuss the role of megakaryocytes (MKs) in thromboinflammation and their adaptive responses.
Keywords: megakaryocytes; platelets; thromboinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Oikonomou E., Leopoulou M., Theofilis P., Antonopoulos A., Siasos G., Latsios G., Mystakidi V.C., Antoniades C., Tousoulis D. A link between inflammation and thrombosis in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases: Clinical and therapeutic implications. Atherosclerosis. 2020;309:16–26. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2020.07.027. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bültmann A., Li Z., Wagner S., Peluso M., Schönberger T., Weis C., Konrad I., Stellos K., Massberg S., Nieswandt B., et al. Impact of glycoprotein VI and platelet adhesion on atherosclerosis—A possible role of fibronectin. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010;49:532–542. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.04.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

