Malonyl/Acetyltransferase (MAT) Knockout Decreases Triacylglycerol and Medium-Chain Fatty Acid Contents in Goat Mammary Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 35564013
- PMCID: PMC9104349
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11091291
Malonyl/Acetyltransferase (MAT) Knockout Decreases Triacylglycerol and Medium-Chain Fatty Acid Contents in Goat Mammary Epithelial Cells
Abstract
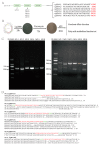
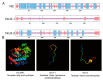
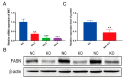
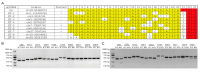
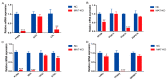
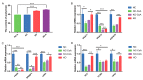
Malonyl/acetyltransferase (MAT) is a crucial functional domain of fatty acid synthase (FASN), which plays a vital role in the de novo synthesis of fatty acids in vivo. Milk fatty acids are secreted by mammary epithelial cells. Mammary epithelial cells are the units of mammary gland development and function, and it is a common model for the study of mammary gland tissue development and lactation. This study aimed to investigate the effects of MAT deletion on the synthesis of triacylglycerol and medium-chain fatty acids. The MAT domain was knocked out by CRISPR/Cas9 in the goat mammary epithelial cells (GMECs), and in MAT knockout GMECs, the mRNA level of FASN was decreased by approximately 91.19% and the protein level decreased by 51.83%. The results showed that MAT deletion downregulated the contents of triacylglycerol and medium-chain fatty acids (p < 0.05) and increased the content of acetyl-Coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) (p < 0.001). Explicit deletion of MAT resulted in significant drop of FASN, which resulted in downregulation of LPL, GPAM, DGAT2, PLIN2, XDH, ATGL, LXRα, and PPARγ genes in GMECs (p < 0.05). Meanwhile, mRNA expression levels of ACC, FASN, DGAT2, SREBP1, and LXRα decreased following treatment with acetyl-CoA (p < 0.05). Our data reveals that FASN plays critical roles in the synthesis of medium-chain fatty acids and triacylglycerol in GMECs.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; FASN; MAT; acetyl-CoA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Goat FADS2 controlling fatty acid metabolism is directly regulated by SREBP1 in mammary epithelial cells.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad030. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad030. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 36694375 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of SREBP1 (sterol regulatory element binding protein 1) promotes de novo fatty acid synthesis and triacylglycerol accumulation in goat mammary epithelial cells.J Dairy Sci. 2016 Jan;99(1):783-95. doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-9736. Epub 2015 Nov 18. J Dairy Sci. 2016. PMID: 26601584
-
Inhibition of FASN reduces the synthesis of medium-chain fatty acids in goat mammary gland.Animal. 2014 Sep;8(9):1469-78. doi: 10.1017/S1751731114001323. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Animal. 2014. PMID: 24909980
-
Effect of short-chain fatty acids on triacylglycerol accumulation, lipid droplet formation and lipogenic gene expression in goat mammary epithelial cells.Anim Sci J. 2016 Feb;87(2):242-9. doi: 10.1111/asj.12420. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Anim Sci J. 2016. PMID: 26304676 Review.
-
Regulation of Key Genes for Milk Fat Synthesis in Ruminants.Front Nutr. 2021 Nov 25;8:765147. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.765147. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34901115 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals the important role of hepatic fatty acid metabolism in the acute heat stress response in chickens.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 2;26(1):631. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11832-2. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40604375 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of emulsifiers on lipid metabolism and performance of yellow-feathered broilers.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Jun 7;20(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04095-8. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38849831 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Variation of CPT1A Induces Lipid Reconstruction in Goat Intramuscular Precursor Adipocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 29;24(17):13415. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713415. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yao D., Luo J., He Q., Shi H., Li J., Wang H., Xu H., Chen Z., Yi Y., Loor J.J. SCD1 Alters Long-Chain Fatty Acid (LCFA) Composition and Its Expression Is Directly Regulated by SREBP-1 and PPARgamma 1 in Dairy Goat Mammary Cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2017;232:635–649. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25469. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

