Nanotechnology-Assisted Cell Tracking
- PMID: 35564123
- PMCID: PMC9103829
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12091414
Nanotechnology-Assisted Cell Tracking
Abstract
The usefulness of nanoparticles (NPs) in the diagnostic and/or therapeutic sector is derived from their aptitude for navigating intra- and extracellular barriers successfully and to be spatiotemporally targeted. In this context, the optimization of NP delivery platforms is technologically related to the exploitation of the mechanisms involved in the NP-cell interaction. This review provides a detailed overview of the available technologies focusing on cell-NP interaction/detection by describing their applications in the fields of cancer and regenerative medicine. Specifically, a literature survey has been performed to analyze the key nanocarrier-impacting elements, such as NP typology and functionalization, the ability to tune cell interaction mechanisms under in vitro and in vivo conditions by framing, and at the same time, the imaging devices supporting NP delivery assessment, and consideration of their specificity and sensitivity. Although the large amount of literature information on the designs and applications of cell membrane-coated NPs has reached the extent at which it could be considered a mature branch of nanomedicine ready to be translated to the clinic, the technology applied to the biomimetic functionalization strategy of the design of NPs for directing cell labelling and intracellular retention appears less advanced. These approaches, if properly scaled up, will present diverse biomedical applications and make a positive impact on human health.
Keywords: cell labelling; cell tracking; cell uptake; nanoparticles; stem cell homing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
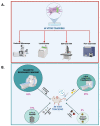
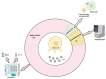
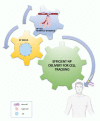
References
-
- Zimmer C., Zhang B., Dufour A., Thebaud A., Berlemont S., Meas-Yedid V., Marin J.-C.O. On the digital trail of mobile cells. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2006;23:54–62. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2006.1628878. - DOI
-
- Meijering E., Smal I., Danuser G. Tracking in molecular bioimaging. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2006;23:46–53. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2006.1628877. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

