Impact of Adsorption of Straight Chain Alcohol Molecules on the Optical Properties of Calcite (10.4) Surface
- PMID: 35564169
- PMCID: PMC9099925
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12091460
Impact of Adsorption of Straight Chain Alcohol Molecules on the Optical Properties of Calcite (10.4) Surface
Abstract
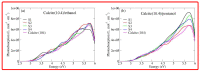
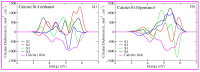
Calcium carbonate plays a central role in controlling the chemistry of the oceans, biomineralization and oil production, to name a few. In this work, using density functional theory with semiempirical dispersion corrections and simplified TD-DFT using Tamm-Dancoff approximation, we investigated the impact of the adsorption of straight chain alcohol (ethanol and pentanol) molecules on the optical properties of a calcite (10.4) surface. Our results show that ethanol and/or pentanol molecules form a well-ordered monolayer (through their hydroxyl group with carbon chains sticking away in a standing-up position) on the calcite (10.4) surface. Additionally, we found intriguing modulations in the photoabsorption spectra and circular dichroism spectra. In particular, the latter was a unique optical fingerprint for a molecule-adsorbed calcite (10.4) surface. Our findings provide useful insights into the structural and optical features of calcite-based systems at the atomic level.
Keywords: DFT; TD-DFT; adsorption; calcite.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Millero F.J. Chemical Oceanography. 4th ed. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2013.
-
- Morse J.W., Mackenzie F.T. Geochemistry of Sedimentary Carbonates. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 1990.
-
- Talham D.R. Biomineralization: Principles and Concepts in Bioinorganic Materials Chemistry Stephen Mann. Oxford University Press, New York, USA, 2001. Cryst. Growth Des. 2002;2:675. doi: 10.1021/cg020033l. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

