Electrohydrodynamics Analysis of Dielectric 2D Nanofluids
- PMID: 35564198
- PMCID: PMC9106012
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12091489
Electrohydrodynamics Analysis of Dielectric 2D Nanofluids
Abstract
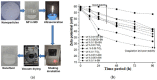
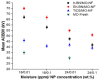
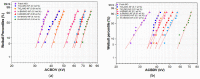
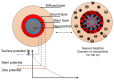
The purpose of this present study is to prepare a stable mineral-oil (MO)-based nanofluid (NF) for usage as a coolant in a transformer. Nanoparticles (NPs) such as hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) and titanium oxide (TiO2) have superior thermal and electrical characteristics. Their dispersion into MO is likely to elevate the electrothermal properties of NFs. Therefore, different batches of NFs are prepared by uniformly dispersing the insulating h-BN and semiconducting TiO2 NP of different concentrations in MO. Bulk h-BN NP of size 1μm is exfoliated into 2D nanosheets of size 150-200 nm, subsequently enhancing the surface area of exfoliated h-BN (Eh-BN). However, from the zeta-potential analysis, NP concentration of 0.01 and 0.1 wt.% are chosen for further study. The thermal conductivity and ACBDV studies of the prepared NF are performed to investigate the cooling and insulation characteristics. The charging-dynamics study verifies the enhancement in ACBDV of the Eh-BN NF. Weibull statistical analysis is carried out to obtain the maximum probability of ACBDV failure, and it is observed that 0.01 wt.% based NF has superior cooling and insulation properties than MO and remaining batches of NFs.
Keywords: 2D nanomaterials; breakdown; charge dynamics; electrophoresis; nanodielectrics; thermal conductivity; voltage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



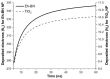
References
-
- Oommen T.V. Moisture equilibrium charts for transformer insulation drying practice. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1984;103:3062–3067. doi: 10.1109/TPAS.1984.318326. - DOI
-
- Hwang J.G., Zahn M., O’Sullivan F.M., Pettersson L.A.A., Hjortstam O., Liu R. Effects of nanoparticle charging on streamer development in transformer oil-based nanofluids. J. Appl. Phys. 2010;107:14310–14317. doi: 10.1063/1.3267474. - DOI
-
- Choi C., Yoo S.H., Oh J.M. Preparation and heat transfer properties of nanoparticle-in-transformer oil dispersions as advanced energy efficient coolants. J. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2008;8:710–712. doi: 10.1016/j.cap.2007.04.060. - DOI
-
- UmerIlyasa S., Pendyalaa R., Naraharib M., Susin L. Stability, rheology and thermal analysis of functionalized alumina- thermal oil-based nanofluids for advanced cooling systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017;142:215–229.
-
- Hussain M., Mir F.A., Ansari M.A. Nanofluid transformer oil for cooling and insulating applications: A brief review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2022;8:100223. doi: 10.1016/j.apsadv.2022.100223. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

