Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide with Hollow Nanostructure for Application to Lithium-Ion Batteries
- PMID: 35564216
- PMCID: PMC9103021
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12091507
Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide with Hollow Nanostructure for Application to Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
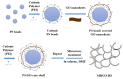
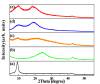
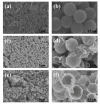
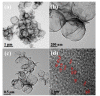
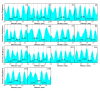
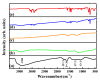
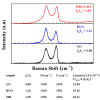
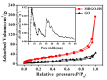
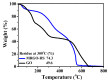
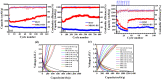
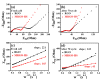
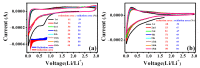
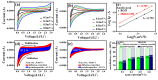
In this study, reduced graphene oxide (RGO) with a hollow nanostructure was successfully synthesized by layer-by-layer self-assembly using electrostatic interactions and van der Waals forces between building blocks, and its lithium storage characteristics were investigated. After 800 cycles at a current density of 1 A/g, the microwave-irradiated RGO hollow spheres (MRGO-HS) maintained a capacity of 626 mA h/g. In addition, when the charge/discharge capacity was measured stepwise in the current density range of 0.1-2 A/g, the discharge capacity of the RGO rapidly decreased to 156 mA h/g even at the current density of 2 A/g, whereas MRGO-HS provided a capacity of 252 mA h/g. Even after the current density was restored at a current density of 0.1 A/g, the MRGO-HS capacity was maintained to be 827 mA h/g at the 100th cycle, which is close to the original reversible capacity. Thus, MRGO-HS provides a higher capacity and better rate capability than those of traditionally synthesized RGO.
Keywords: Exfoliation; hollow spheres; layer-by-layer self-assembly; lithium-ion batteries; reduced graphene oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. And the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Peng K., Jie J., Zhang W., Lee S.-T. Silicon nanowires for rechargeable lithium-ion battery anodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008;93:033105. doi: 10.1063/1.2929373. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

