N-Rich Doped Anatase TiO2 with Smart Defect Engineering as Efficient Photocatalysts for Acetaldehyde Degradation
- PMID: 35564273
- PMCID: PMC9105496
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12091564
N-Rich Doped Anatase TiO2 with Smart Defect Engineering as Efficient Photocatalysts for Acetaldehyde Degradation
Abstract
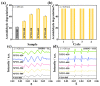
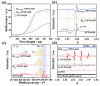
Nitrogen (N) doping is an effective strategy for improving the solar-driven photocatalytic performance of anatase TiO2, but controllable methods for nitrogen-rich doping and associated defect engineering are highly desired. In this work, N-rich doped anatase TiO2 nanoparticles (4.2 at%) were successfully prepared via high-temperature nitridation based on thermally stable H3PO4-modified TiO2. Subsequently, the associated deep-energy-level defects such as oxygen vacancies and Ti3+ were successfully healed by smart photo-Fenton oxidation treatment. Under visible-light irradiation, the healed N-doped TiO2 exhibited a ~2-times higher activity of gas-phase acetaldehyde degradation than the non-treated one and even better than standard P25 TiO2 under UV-visible-light irradiation. The exceptional performance is attributed to the extended spectral response range from N-rich doping, the enhanced charge separation from hole capturing by N-doped species, and the healed defect levels with the proper thermodynamic ability for facilitating O2 reduction, depending on the results of ∙O2- radicals and defect measurement by electron spin resonance, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, atmosphere-controlled surface photovoltage spectra, etc. This work provides an easy and efficient strategy for the preparation of high-performance solar-driven TiO2 photocatalysts.
Keywords: N-rich doping; anatase TiO2; charge separation; defect healing; photocatalytic acetaldehyde degradation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Crespo-Monteiro N., Hamandi M., Higuita M.A.U., Guillard C., Dappozze F., Jamon D., Vocanson F., Jourlin Y. Influence of the Micro-Nanostructuring of Titanium Dioxide Films on the Photocatalytic Degradation of Formic Acid under Uv Illumination. Nanomaterials. 2022;12:1008. doi: 10.3390/nano12061008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hunge Y.M., Yadav A.A., Dhodamani A.G., Suzuki N., Terashima C., Fujishima A., Mathe V.L. Enhanced photocatalytic performance of ultrasound treated GO/TiO2 composite for photocatalytic degradation of salicylic acid under sunlight illumination. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020;61:104849. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104849. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

