Polyethylenimine-Coated Ultrasmall Holmium Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Cytotoxicities, and Water Proton Spin Relaxivities
- PMID: 35564300
- PMCID: PMC9101814
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12091588
Polyethylenimine-Coated Ultrasmall Holmium Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Cytotoxicities, and Water Proton Spin Relaxivities
Abstract
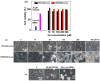
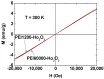
Water proton spin relaxivities, colloidal stability, and biocompatibility of nanoparticle magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents depend on surface-coating ligands. In this study, hydrophilic and biocompatible polyethylenimines (PEIs) of different sizes (Mn = 1200 and 60,000 amu) were used as surface-coating ligands for ultrasmall holmium oxide (Ho2O3) nanoparticles. The synthesized PEI1200- and PEI60000-coated ultrasmall Ho2O3 nanoparticles, with an average particle diameter of 2.05 and 1.90 nm, respectively, demonstrated low cellular cytotoxicities, good colloidal stability, and appreciable transverse water proton spin relaxivities (r2) of 13.1 and 9.9 s-1mM-1, respectively, in a 3.0 T MR field with negligible longitudinal water proton spin relaxivities (r1) (i.e., 0.1 s-1mM-1) for both samples. Consequently, for both samples, the dose-dependent contrast changes in the longitudinal (R1) and transverse (R2) relaxation rate map images were negligible and appreciable, respectively, indicating their potential as efficient transverse T2 MRI contrast agents in vitro.
Keywords: Ho2O3; cytotoxicity; polyethylenimine coating; relaxivity; ultrasmall nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hydrophilic Biocompatible Poly(Acrylic Acid-co-Maleic Acid) Polymer as a Surface-Coating Ligand of Ultrasmall Gd2O3 Nanoparticles to Obtain a High r1 Value and T1 MR Images.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Dec 22;11(1):2. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11010002. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33375089 Free PMC article.
-
Water-soluble d-glucuronic acid coated ultrasmall mixed Ln/Mn (Ln = Gd and Dy) oxide nanoparticles and their application to magnetic resonance imaging.Biomater Sci. 2014 Sep 29;2(9):1287-1295. doi: 10.1039/c4bm00107a. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Biomater Sci. 2014. PMID: 32481899
-
New Class of Efficient T2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent: Carbon-Coated Paramagnetic Dysprosium Oxide Nanoparticles.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Oct 15;13(10):312. doi: 10.3390/ph13100312. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33076332 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, Magnetic Properties, Map Images, and Water Proton Relaxivities of D-Glucuronic Acid Coated Ln2O3 Nanoparticles (Ln = Ho and Er).J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015 Sep;15(9):7311-6. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2015.10582. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26716328
-
Ultrasmall Europium, Gadolinium, and Dysprosium Oxide Nanoparticles: Polyol Synthesis, Properties, and Biomedical Imaging Applications.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020;20(17):1767-1780. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666200604163452. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32496986 Review.
Cited by
-
Polyethylenimine as a Non-Innocent Ligand for Hexacyanoferrates Immobilization.Molecules. 2022 Dec 2;27(23):8489. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238489. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500581 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Applications of Rare Earth Metal Nanoparticles in Biomedicine.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 24;18(2):154. doi: 10.3390/ph18020154. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40005968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of miR-199a-5p-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticle-polyethyleneimine-KALA in osteogenic differentiation.J Dent Sci. 2024 Jul;19(3):1506-1514. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2024.01.007. Epub 2024 Feb 5. J Dent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39035341 Free PMC article.
-
Special Issue "Advanced Nanomaterials for Bioimaging".Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jul 20;12(14):2496. doi: 10.3390/nano12142496. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35889719 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based High-Performance Positive and Negative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 15;15(6):1745. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061745. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376193 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roch A., Gillis P., Muller R.N. Theory of proton relaxation induced by superparamagnetic particles. J. Chem. Phys. 1999;110:5403–5411. doi: 10.1063/1.478435. - DOI
-
- Lauffer R.B. Paramagnetic metal complexes as water proton relaxation agents for NMR imaging: Theory and design. Chem. Rev. 1987;87:901–927. doi: 10.1021/cr00081a003. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

