Cyanine-Doped Nanofiber Mats for Laser Tissue Bonding
- PMID: 35564323
- PMCID: PMC9105542
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12091613
Cyanine-Doped Nanofiber Mats for Laser Tissue Bonding
Abstract
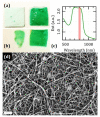
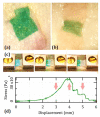
In spite of an extensive body of academic initiatives and innovative products, the toolkit of wound dressing has always revolved around a few common concepts such as adhesive patches and stitches and their variants. Our work aims at an alternative solution for an immediate restitutio ad integrum of the mechanical functionality in cutaneous repairs. We describe the fabrication and the application of electrospun mats of bioactive nanofibers all made of biocompatible components such as a natural polysaccharide and a cyanine dye for use as laser-activatable plasters, resembling the ultrastructure of human dermis. In particular, we investigate their morphological features and mechanical moduli under conditions of physiological relevance, and we test their use to bind a frequent benchmark of connective tissue as rabbit tendon and a significant case of clinical relevance as human dermis. Altogether, our results point to the feasibility of a new material for wound dressing combining translational potential, strength close to human dermis, extensibility exceeding 15% and state-of-art adhesive properties.
Keywords: chitosan; dermis; electrospun nanofibers; indocyanine green; wound dressing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Wound dressing based on electrospun PVA/chitosan/starch nanofibrous mats: Fabrication, antibacterial and cytocompatibility evaluation and in vitro healing assay.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Feb 1;122:238-254. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.115. Epub 2018 Oct 18. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30342125
-
Pectinate nanofiber mat with high absorbency and antibacterial activity: A potential superior wound dressing to alginate and chitosan nanofiber mats.Carbohydr Polym. 2017 Oct 15;174:591-600. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.096. Epub 2017 Jun 24. Carbohydr Polym. 2017. PMID: 28821109
-
Electrospun poly(l-lactide)/zein nanofiber mats loaded with Rana chensinensis skin peptides for wound dressing.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016 Sep;27(9):136. doi: 10.1007/s10856-016-5749-7. Epub 2016 Jul 18. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016. PMID: 27432415
-
An Overview on Application of Natural Substances Incorporated with Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffolds to Development of Innovative Wound Dressings.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018 Feb 14;18(5):414-427. doi: 10.2174/1389557517666170308112147. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28271816 Review.
-
Delivery of Therapeutics from Layer-by-Layer Electrospun Nanofiber Matrix for Wound Healing: An Update.J Pharm Sci. 2021 Feb;110(2):635-653. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2020.10.003. Epub 2020 Oct 9. J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 33039441 Review.
Cited by
-
Preliminary Evaluation of 3D-Printed Alginate/Gelatin Scaffolds for Protein Fast Release as Suitable Devices for Personalized Medicine.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 2;13(6):1365. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061365. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kamoun E.A., Chen X., Eldin M.S.M., Kenawy E.R.S. Crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels for wound dressing applications: A review of remarkably blended polymers. Arab. J. Chem. 2015;8:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.07.005. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

