Mental Health Outcomes in Australian Healthcare and Aged-Care Workers during the Second Year of the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 35564351
- PMCID: PMC9103405
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19094951
Mental Health Outcomes in Australian Healthcare and Aged-Care Workers during the Second Year of the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Objective: the COVID-19 pandemic has incurred psychological risks for healthcare workers (HCWs). We established a Victorian HCW cohort (the Coronavirus in Victorian Healthcare and Aged-Care Workers (COVIC-HA) cohort study) to examine COVID-19 impacts on HCWs and assess organisational responses over time.
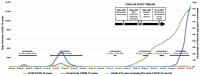
Methods: mixed-methods cohort study, with baseline data collected via an online survey (7 May-18 July 2021) across four healthcare settings: ambulance, hospitals, primary care, and residential aged-care. Outcomes included self-reported symptoms of depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress (PTS), wellbeing, burnout, and resilience, measured using validated tools. Work and home-related COVID-19 impacts and perceptions of workplace responses were also captured.
Results: among 984 HCWs, symptoms of clinically significant depression, anxiety, and PTS were reported by 22.5%, 14.0%, and 20.4%, respectively, highest among paramedics and nurses. Emotional exhaustion reflecting moderate-severe burnout was reported by 65.1%. Concerns about contracting COVID-19 at work and transmitting COVID-19 were common, but 91.2% felt well-informed on workplace changes and 78.3% reported that support services were available.
Conclusions: Australian HCWs employed during 2021 experienced adverse mental health outcomes, with prevalence differences observed according to occupation. Longitudinal evidence is needed to inform workplace strategies that support the physical and mental wellbeing of HCWs at organisational and state policy levels.
Keywords: COVID-19; healthcare workers; infectious diseases epidemiology; occupational health; psychological disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Australian Bureau of Statistics Regional Population. ABS; 2019-20 [Updated 30 March 2021] [(accessed on 5 October 2021)]; Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/regional-population/....
-
- Victorian Department of Health COVID-19 Writing Group Population-based analysis of the epidemiological features of COVID-19 epidemics in Victoria, Australia, January 2020–March 2021, and their suppression through comprehensive control strategies. Lancet Reg. Health West Pac. 2021;17:100297. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2021.100297. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . [(accessed on 21 March 2022)]. Weekly Operational Update on COVID-19—29 December 2020. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update---....
-
- De Foo C., Grépin K.A., Cook A.R., Hsu L.Y., Bartos M., Singh S., Asgari N., Teo Y.Y., Heymann D.L., Legido-Quigley H. Navigating from SARS-CoV-2 elimination to endemicity in Australia, Hong Kong, New Zealand, and Singapore. Lancet. 2021;398:1547–1551. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02186-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

