How the COVID-19 Pandemic Affects Risk Awareness in Dentists: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 35564366
- PMCID: PMC9103177
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19094971
How the COVID-19 Pandemic Affects Risk Awareness in Dentists: A Scoping Review
Abstract
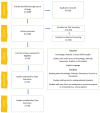
Dentists are on the frontline of infection, especially when it comes to respiratory viruses like the new coronavirus. The purpose of this paper is to conduct a scoping review to better understand dentists' risk awareness, awareness of COVID-19 symptoms, preventive measures, and effective methods of COVID-19 infection prevention and management. This paper systematically assesses the published literature on dentistry and COVID-19. Various electronic databases including Ovid MEDLINE, Scopus, Embase, and MEDLINE via PubMed were searched up to 9 September 2021. Overall, 39 papers were included. Almost the entirety of dentists (94.5%) reported awareness of the three most common COVID-19 symptoms, and a risk awareness score of about 90% was shown, while 88.2% of dentists reported adopting preventive measures. More than 50% did not want to treat infected people. While 70.3% of dentists recommended usage of N95 masks, the rate of dentists using them was below 40%. Sufficient awareness of risks during the pandemic was found in dentists. Although they were using preventive measures, there remains upside potential for adopting all recommended measures. Further, the usage of N95 masks is improvable, even though the benefit of wearing them could not be confirmed.
Keywords: COVID-19; dentist; dentistry; review; risk awareness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. [(accessed on 28 March 2022)]. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/cases-2019-ncov-eueea.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO): Coronavirus Disease (COVID-2019) Advice for the Public. [(accessed on 28 March 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical