Interaction between Digital Economy and Environmental Pollution: New Evidence from a Spatial Perspective
- PMID: 35564469
- PMCID: PMC9102385
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19095074
Interaction between Digital Economy and Environmental Pollution: New Evidence from a Spatial Perspective
Abstract
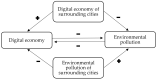
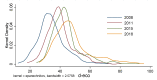
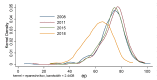
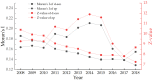
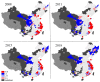
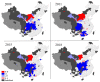
The digital economy and the green economy are two major issues for economic recovery in the post epidemic era. From spatial interaction spillover, we analyze and measure the relationships between the digital economy and environmental pollution in 287 prefecture-level cities in China from 2008 to 2018 using simultaneous spatial equations and the generalized 3-stage least square (GS3SLS) method. The results show that: (1) there is a reverse and complex spatio-temporal evolution of the digital economy and environmental pollution in Chinese cities. (2) There is a spatial interaction spillover effect between the digital economy and environmental pollution. Local digital economy and environmental pollution inhibit each other. The digital economy and environmental pollution have a significant spatial spillover. The digital economy of surrounding regions has a suppressive effect on local environmental pollution. The environmental pollution of surrounding cities has a crowding-out effect on the local digital economy. (3) Digital economy suppresses environmental pollution through the green development effect and innovative development effect; environmental pollution suppresses the digital economy through the talent crowding out effect and the policy tightening effect. The conclusion of this paper provides evidence for the coupling and coordinated development between the digital and green economy, which is of great significance for promoting the transformation of economic development modes and realizing green and high-quality development.
Keywords: GS3SLS; digital economy; environmental pollution; green economy; simultaneous spatial equation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spatial Interaction Spillover Effects between Digital Financial Technology and Urban Ecological Efficiency in China: An Empirical Study Based on Spatial Simultaneous Equations.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 12;18(16):8535. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18168535. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34444283 Free PMC article.
-
Path to pollution and carbon reduction synergy from the perspective of the digital economy: Fresh evidence from 292 prefecture-level cities in China.Environ Res. 2024 Jul 1;252(Pt 4):119050. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.119050. Epub 2024 May 8. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 38729414 Review.
-
Impact of digital economic development and environmental pollution on residents' health: an empirical analysis based on 279 prefecture-level cities in China.BMC Public Health. 2023 May 26;23(1):959. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15788-4. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37231366 Free PMC article.
-
Digital economy development and haze pollution: evidence from China.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Oct;29(48):73210-73226. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-20957-w. Epub 2022 May 27. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35622289
-
The Impact of Haze Pollution on Regional Eco-Economic Treatment Efficiency in China: An Environmental Regulation Perspective.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Oct 23;16(21):4059. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16214059. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31652690 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of digital inclusive finance on environmental pollution: A case study of air pollution.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 24;19(7):e0305963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305963. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39047026 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of the digital economy on high-quality agricultural development--Based on the regulatory effects of financial development.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 6;19(3):e0293538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293538. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38446805 Free PMC article.
-
Novel enterprises digital transformation influence empirical study.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 12;19(1):e0296693. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296693. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38215168 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Digital Transformation on Enterprise Carbon Intensity: The Moderating Role of Digital Information Resources.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 25;20(3):2178. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20032178. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767545 Free PMC article.
-
Digital economy and green total factor productivity in China.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 1;19(3):e0299716. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299716. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38427655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lu Z.-N., Chen H., Hao Y., Wang J., Song X., Mok T.M. The dynamic relationship between environmental pollution, economic development and public health: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017;166:134–147. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.08.010. - DOI
-
- Liang W., Yang M. Urbanization, economic growth and environmental pollution: Evidence from China. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2019;21:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.suscom.2018.11.007. - DOI
-
- Liao G., Drakeford B.M. An analysis of financial support, technological progress and energy efficiency:evidence from China. Green Financ. 2019;1:174–187. doi: 10.3934/GF.2019.2.174. - DOI
-
- Zheng Y., Chen S., Wang N. Does financial agglomeration enhance regional green economy development? Evidence from China. Green Financ. 2020;2:173–196. doi: 10.3934/GF.2020010. - DOI
-
- Hao Y., Zheng S., Zhao M., Wu H., Guo Y., Li Y. Reexamining the relationships among urbanization, industrial structure, and environmental pollution in China—New evidence using the dynamic threshold panel model. Energy Rep. 2020;6:28–39. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2019.11.029. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

