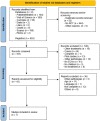
Robotic Systems for the Physiotherapy Treatment of Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35564511
- PMCID: PMC9100658
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19095116
Robotic Systems for the Physiotherapy Treatment of Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Cerebral palsy is a neurological condition that is associated with multiple motor alterations and dysfunctions in children. Robotic systems are new devices that are becoming increasingly popular as a part of the treatment for cerebral palsy. A systematic review of the Pubmed, Web of Science, MEDLINE, Cochrane, Dialnet, CINAHL, Scopus, Lilacs and PEDro databases from November 2021 to February 2022 was conducted to prove the effectiveness of these devices for the treatment of motor dysfunctions in children who were diagnosed with cerebral palsy. Randomized clinical trials in Spanish and English were included. In total, 653 potential manuscripts were selected but only 7 of them met the inclusion criteria. Motor dysfunctions in the lower limbs and those that are specifically related to gait are the main parameters that are affected by cerebral palsy and the robotic systems Lokomat, Innowalk, Robogait and Waltbox-K are the most commonly used. There is no consensus about the effectiveness of these devices. However, it seems clear that they have presented a good complement to conventional physical therapies, although not a therapy as themselves. Unfortunately, the low quality of some of the randomized clinical trials that were reviewed made it difficult to establish conclusive results. More studies are needed to prove and test the extent to which these devices aid in the treatment of children with cerebral palsy.
Keywords: cerebral palsy; children; physiotherapy treatments; robotic systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(26):1-149. doi: 10.3310/hta5260. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701099
-
Surgical treatment for the thumb-in-palm deformity in patients with cerebral palsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Oct 19;2005(4):CD004093. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004093.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16235349 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Psychological and/or educational interventions for the prevention of depression in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD003380. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003380.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 07;(12):CD003380. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003380.pub3. PMID: 14974014 Updated.
Cited by
-
Robot-assisted upper limb therapy for personalized rehabilitation in children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review.Front Neurol. 2025 Jan 6;15:1499249. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1499249. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39835154 Free PMC article.
-
Benefits of robotic gait assistance with ATLAS 2030 in children with cerebral palsy.Front Pediatr. 2024 Jul 29;12:1398044. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1398044. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39135857 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Robotic Devices for Medical Rehabilitation: An Umbrella Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Nov 4;13(21):6616. doi: 10.3390/jcm13216616. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39518755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneity of Attitudes toward Robots in Healthcare among the Chinese Public: A Latent Profile Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 28;20(1):508. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010508. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36612827 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture and Acupoints for Managing Pediatric Cerebral Palsy: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Sep 5;12(17):1780. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12171780. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39273805 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rosenbaum P., Paneth N., Leviton A., Goldstein M., Bax M., Damiano D., Dan B., Jacobsson B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. Suppl. 2007;49:8–14. - PubMed
-
- Novak I., Morgan C., Adde L., Blackman J., Boyd R.N., Brunstrom-Hernandez J., Cioni G., Damiano D., Darrah J., Eliasson A.C., et al. Early, accurate diagnosis and early intervention in cerebral palsy: Advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171:897–907. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.1689. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous