The Health-Sustaining, Moderating, and Mediating Roles of Sense of Coherence in the Relationship between Fear of COVID-19 and Burnout among South African Teachers
- PMID: 35564555
- PMCID: PMC9100965
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19095160
The Health-Sustaining, Moderating, and Mediating Roles of Sense of Coherence in the Relationship between Fear of COVID-19 and Burnout among South African Teachers
Abstract
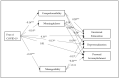
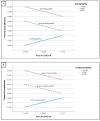
The current study focuses on the interrelationship between fear of COVID-19, sense of coherence, and burnout. Participants (n = 355) were school teachers from across all provinces in South Africa who completed the Fear of COVID-19 Scale, the Sense of Coherence Scale, and the Maslach Burnout Inventory. It was hypothesized that the dimensions of sense of coherence would be directly associated with burnout and would also mediate or moderate the relationship between fear of COVID-19 and burnout. The results of the path and moderation analyses conducted confirmed this hypothesis. In particular, the health-sustaining role of sense of coherence was demonstrated through the significant direct associations between comprehensibility and manageability on one hand and emotional exhaustion, as well as depersonalization, on the other hand. In addition, meaningfulness had significant direct associations with emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and personal accomplishment. Meaningfulness mediated the relationship between fear of COVID-19 and all burnout subscales, while comprehensibility and manageability only mediated the relationship between fear of COVID-19 and both emotional exhaustion and depersonalization. However, comprehensibility and manageability played a moderating role in the relationship between fear of COVID-19 and personal accomplishment. These findings confirm the crucial role of protective factors, such as sense of coherence, and highlights the need for interventions that could strengthen these resources within teachers.
Keywords: comprehensibility; depersonalization; emotional exhaustion; fear of COVID-19; manageability; meaningfulness; personal accomplishment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Facing Your Fear of COVID-19: Resilience as a Protective Factor Against Burnout in South African Teachers.Ann Med Psychol (Paris). 2023 Feb;181(2):119-127. doi: 10.1016/j.amp.2022.05.001. Epub 2022 May 11. Ann Med Psychol (Paris). 2023. PMID: 35573929 Free PMC article.
-
Sense of Coherence and Burnout in Healthcare Professionals in the COVID-19 Era.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Aug 2;12:709587. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.709587. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34408684 Free PMC article.
-
The mediational effect of coherence on the relationship between mental load and job burnout among oncology nurses.Int J Nurs Pract. 2019 Jun;25(3):e12736. doi: 10.1111/ijn.12736. Epub 2019 May 14. Int J Nurs Pract. 2019. PMID: 31087514
-
Prevalence of burnout syndrome in oncology nursing: A meta-analytic study.Psychooncology. 2018 May;27(5):1426-1433. doi: 10.1002/pon.4632. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Psychooncology. 2018. PMID: 29314432 Review.
-
[Burnout: rising interest phenomenon in stressful workplace].Ann Ig. 2006 Mar-Apr;18(2):171-7. Ann Ig. 2006. PMID: 16649514 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
The impact of childhood trauma on emotional distress and the moderating role of sense of coherence among college students in China.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 29;14(1):9797. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60537-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38684905 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spaull N., van der Berg S. Counting the cost: COVID-19 school closures in South Africa and its impact on children. S. Afr. J. Child. Educ. 2020;10:1–13. doi: 10.4102/sajce.v10i1.924. - DOI
-
- van der Walt P.J.L., Oosthuizen P.I.J. The opening and reopening of schools in South Africa during the COVID-19 pandemic: An appraisal from two vantage points. Perspect. Educ. 2021;39:29–43. doi: 10.18820/2519593X/pie.v39.i1.3. - DOI
-
- MacIntyre P.D., Gregersen T., Mercer S. Language teachers’ coping strategies during the COVID-19 conversion to online teaching: Correlations with stress, wellbeing and negative emotions. System. 2020;94:102352. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2020.102352. - DOI
-
- Shepherd D., Mohohlwane N. The impact of COVID-19 in education—More than a year of disruption. [(accessed on 14 April 2022)];Natl. Income Dyn. (NIDS)-Coronavirus Rapid Mob. Surv. (CRAM) Wave. 2021 5 Available online: https://cramsurvey.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/11.-Shepherd-D-_-Mohoh....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

