Nonverbal Oro-Motor Exercises: Do They Really Work for Phonoarticulatory Difficulties?
- PMID: 35564854
- PMCID: PMC9104859
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19095459
Nonverbal Oro-Motor Exercises: Do They Really Work for Phonoarticulatory Difficulties?
Abstract
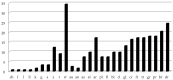
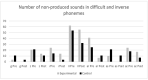
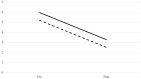
Articulation disorders are deficiencies in the realization of speech sounds unrelated to organic or neurological disorders. Over the last decade, there has been a debate on the efficiency of non-verbal oro-motor exercises, which are orofacial movements programmed and organized in an intentional and coordinated way to control lips, tongue, and soft palate muscles. Of the 122 children evaluated, 52 presented articulatory difficulties. An intervention with nonverbal oro-motor exercises was applied, and children were again assessed following treatment. The results showed no differences between the experimental and control groups, either in the number of sounds that improved after this period or in the severity of difficulties (we categorized those with articulation difficulties in two to six sounds as 'medium' and those with difficulties in articulating more than seven sounds as 'severe'). These results indicated that nonverbal oro-motor exercises alone are not efficient for intervention in difficulties in the realization of sounds in 4-year-old children.
Keywords: articulation disorder; childhood; intervention in difficulties in articulation; nonverbal oro-motor exercises; phonetic disorder; practice-based evidence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Electropalatography in the treatment of articulation/phonological disorders.J Commun Disord. 1995 Dec;28(4):303-29. doi: 10.1016/0021-9924(95)00059-1. J Commun Disord. 1995. PMID: 8576412
-
Are oral-motor exercises useful in the treatment of phonological/articulatory disorders?Semin Speech Lang. 2002 Feb;23(1):15-26. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-23508. Semin Speech Lang. 2002. PMID: 11938488 Review.
-
Speech modification by a deaf child through dynamic orometric modeling and feedback.J Speech Hear Disord. 1983 May;48(2):178-85. doi: 10.1044/jshd.4802.178. J Speech Hear Disord. 1983. PMID: 6621010
-
[Clinical characteristics and speech therapy of lingua-apical articulation disorder].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Mar;44(3):210-3. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16624061 Chinese.
-
What works: evidence-based intervention for children with speech sound disorders.Semin Speech Lang. 2008 Nov;29(4):320-30. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1103396. Epub 2008 Dec 4. Semin Speech Lang. 2008. PMID: 19058119 Review.
References
-
- American Psychiatry Association . DSM-5. Manual Diagnóstico y Estadístico de los Trastornos Mentales. Editorial Médica Panamericana; Madrid, Spain: 2013.
-
- Hidalgo A., Quilis M. La voz del Lenguaje: Fonética y Fonología del Español. Prosopopeya; Valencia, Spain: 2012.
-
- De las Heras G., Rodríguez L. Guía de Intervención Logopédica en las Dislalias. Editorial Síntesis; Madrid, Spain: 2015.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

