Can Financial Institutional Deepening and Renewable Energy Consumption Lower CO2 Emissions in G-10 Countries: Fresh Evidence from Advanced Methodologies
- PMID: 35564938
- PMCID: PMC9103211
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19095544
Can Financial Institutional Deepening and Renewable Energy Consumption Lower CO2 Emissions in G-10 Countries: Fresh Evidence from Advanced Methodologies
Abstract
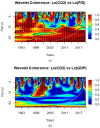
To tackle the challenges associated with global warming and climate change, several countries set their targets to lower carbon emissions in accordance with COP21 (Paris Conference). Even though studies highlighted the different aspects that contribute to environmental degradation, there still exists the scarcity of adequate research that emphasizes the environmental implications of financial institutional deepening, renewable energy consumption (REC), and technology innovations. Therefore, this study investigated the significance of financial institutional deepening, REC, gross domestic product (GDP), imports, exports, and technology innovations to achieve sustainability in G-10 countries, namely The Netherlands, Germany, France, Switzerland, United Kingdom, Sweden, Japan, Belgium, Canada, and Italy from 1990 to 2020. The results obtained from cross-sectionally augmented autoregressive distributed lag (CS-ARDL) and the dynamic common correlated effects mean group (DCCEMG) models reveal that financial institutional deepening and imports positively impact CO2 emissions (CO2e) both in the long and short run. A 1% increase in financial institutional deepening and import will increase CO2e by 0.5403% and 0.2942% in the short run and 0.2980% and 0.1479% in the long run levels, respectively. Contrary to this, REC, GDP, exports, and technology innovations improve environmental quality in these countries. The Dumitrescu & Hurlin causality test shows bidirectional causality between imports and CO2e, GDP and CO2e, exports and CO2e, and financial institutional deepening and CO2e, compared to unidirectional causality from technology innovations to CO2e and from REC to CO2e. Apart from this, the outcomes suggest that policymakers in G-10 countries have to consider their financial markets and firms to revise their current environmental policies.
Keywords: CO2 emissions; G-10 countries; GDP; financial institutional deepening; renewable energy consumption.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Jian J., Fan X., He P., Xiong H., Shen H. The Effects of Energy Consumption, Economic Growth and Financial Development on CO2 Emissions in China: A VECM Approach. Sustainability. 2019;11:4850. doi: 10.3390/su11184850. - DOI
-
- Musah M., Owusu-Akomeah M., Boateng F., Iddris F., Mensah I.A., Antwi S.K., Agyemang J.K. Long-run equilibrium relationship between energy consumption and CO2 emissions: A dynamic heterogeneous analysis on North Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021;29:10416–10433. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16360-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y., Ramzan M., Adebayo T.S., Oladipupo S.D., Adeshola I., Agyekum E.B. Role of Renewable Energy Consumption and Technological Innovation to Achieve Carbon Neutrality in Spain: Fresh Insights from Wavelet Coherence and Spectral Causality Approaches. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021;9:769067. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2021.769067. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

