Bibliometric Analysis and Literature Review of Tourism Destination Resilience Research
- PMID: 35564957
- PMCID: PMC9105207
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19095562
Bibliometric Analysis and Literature Review of Tourism Destination Resilience Research
Abstract
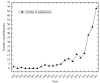
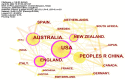
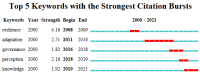
The application of resilience thinking to tourism destination research is a new perspective on sustainable tourism and has gradually become a popular research topic. Some literature has been conducted on tourism destination resilience, but there has not been a comprehensive review and analysis of the whole field. This study was based on the literature from 2000 to 2021 in the Web of Science core collection database. The collaboration analysis, literature co-citation analysis, keyword co-occurrence, burst detection analysis in CiteSpace, and qualitative analysis were adopted to conduct a holistic tourism destination resilience research review. The results indicated that the United States, Australia, China, and the United Kingdom were the primary countries involved in tourism destination resilience research. Five hot research themes were obtained. (1) concept and connotation of tourism destination resilience, (2) drivers of tourism destination resilience, (3) sustainable management framework and practices, (4) perception of tourism destination resilience, and (5) the resilience of the tourism community. Furthermore, four research gaps and future directions were proposed in this study, including the theoretical framework of tourism destination resilience, assessment of tourism destination resilience, sustainable management and resilience, and application of advanced technology in tourism destination resilience. This study assists researchers in understanding the development and future research directions in tourism destination resilience research.
Keywords: CiteSpace; bibliometric analysis; future research directions; research hotspots; tourism destination resilience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Past, current, and future perspectives on eco-tourism: a bibliometric review between 2001 and 2018.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Jul;27(19):23514-23528. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08584-9. Epub 2020 Apr 19. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32307679 Review.
-
Bibliometric analysis of global research trends on male osteoporosis: a neglected field deserves more attention.Arch Osteoporos. 2021 Oct 11;16(1):154. doi: 10.1007/s11657-021-01016-2. Arch Osteoporos. 2021. PMID: 34632530 Review.
-
Understanding Family Tourism: A Perspective of Bibliometric Review.Front Psychol. 2022 Jul 4;13:937312. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.937312. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35859832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review of tourism-environmental degradation nexus.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Nov;28(41):58241-58257. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14798-2. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34110589
-
Global Research on Cognitive Frailty: A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis of Papers Published during 2013-2021.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 4;19(13):8170. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19138170. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35805829 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Spatio-temporal evolution of social-ecological system resilience in ethnic tourism destinations in mountainous areas and trend prediction: a case study in Wuling, China.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 9;14(1):23563. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75023-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39384855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holling C.S. Understanding the complexity of economic, ecological, and social systems. Ecosystems. 2001;4:390–405. doi: 10.1007/s10021-001-0101-5. - DOI
-
- Wall G. Book Review. Tour. Manag. 2018;69:538–539. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2018.07.003. - DOI
-
- Jiang Y.W., Ritchie B.W., Verreynne M.L. Developing disaster resilience: A processual and reflective approach. Tour. Manag. 2021;87:104374. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2021.104374. - DOI
-
- Pyke J., De Lacy T., Law A., Jiang M. Building small destination resilience to the impact of bushfire: A case study. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2016;28:49–58. doi: 10.1016/j.jhtm.2016.04.003. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

