Investigation of the Relationship between Lean Muscle Mass and Erythropoietin Resistance in Maintenance Haemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 35565102
- PMCID: PMC9100199
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19095704
Investigation of the Relationship between Lean Muscle Mass and Erythropoietin Resistance in Maintenance Haemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
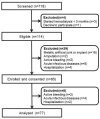
Each patient undergoing maintenance haemodialysis (MHD) has a different response to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs). Haemodilution due to fluid overload has been shown to contribute to anaemia. Body mass index (BMI) has been shown to influence ESA response in dialysis patients; however, BMI calculation does not distinguish between fat and lean tissue. The association between lean muscle mass and erythropoietin hyporesponsiveness is still not well-known among MHD patients. We designed a cross-sectional study and used bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) to analyse the relationship between body composition, haemoglobin level, and erythropoietin resistance index (ERI) in MHD patients. Seventy-seven patients were enrolled in the study group. Compared with patients with haemoglobin ≥ 10 g/dL, those with haemoglobin < 10 g/dL had higher serum ferritin levels, malnutrition−inflammation scores (MIS), relative overhydration, ESA doses, and ERIs. In multivariate logistic regression, higher ferritin levels and MIS were the only predictors of lower haemoglobin levels. The ERI was significantly positively correlated with age, Kt/V, ferritin levels, and MIS and negatively correlated with albumin levels, BMI, and lean tissue index (LTI). Multivariate linear regression analysis revealed that ferritin levels, BMI, and LTI were the most important predictors of ERI. In MHD patients, using BIS to measure body composition can facilitate the development of early interventions that aim to prevent sarcopenia, support ESA responsiveness, and, consequently, improve anaemia management.
Keywords: anaemia; bioimpedance spectroscopy; erythropoietin resistance; haemodialysis; haemoglobin; lean muscle mass; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Simpson J.A., Lobo D.N., Anderson J.A., Macdonald I.A., Perkins A.C., Neal K.R., Allison S.P., Rowlands B.J. Body water compartment measurements: A comparison of bioelectrical impedance analysis with tritium and sodium bromide dilution techniques. Clin. Nutr. 2001;20:339–343. doi: 10.1054/clnu.2001.0398. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous