Machine-Learning-Based Clinical Biomarker Using Cell-Free DNA for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
- PMID: 35565192
- PMCID: PMC9103537
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14092061
Machine-Learning-Based Clinical Biomarker Using Cell-Free DNA for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
Abstract
(1) Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death worldwide. Although various serum enzymes have been utilized for the diagnosis and prognosis of HCC, the currently available biomarkers lack the sensitivity needed to detect HCC at early stages and accurately predict treatment responses. (2) Methods: We utilized our highly sensitive cell-free DNA (cfDNA) detection system, in combination with a machine learning algorithm, to provide a platform for improved diagnosis and prognosis of HCC. (3) Results: cfDNA, specifically alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) expression in captured cfDNA, demonstrated the highest accuracy for diagnosing malignancies among the serum/plasma biomarkers used in this study, including AFP, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, albumin, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin. The diagnostic/prognostic capability of cfDNA was further improved by establishing a cfDNA score (cfDHCC), which integrated the total plasma cfDNA levels and cfAFP-DNA expression into a single score using machine learning algorithms. (4) Conclusion: The cfDHCC score demonstrated significantly improved accuracy in determining the pathological features of HCC and predicting patients' survival outcomes compared to the other biomarkers. The results presented herein reveal that our cfDNA capture/analysis platform is a promising approach to effectively utilize cfDNA as a biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of HCC.
Keywords: cell-free DNA (cfDNA); circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA); hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); liquid biopsy; principal component analysis (PCA).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
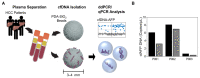
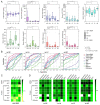
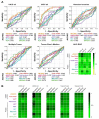
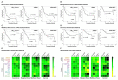
References
-
- Akinyemiju T., Abera S., Ahmed M., Alam N., Alemayohu M.A., Allen C., Al-Raddadi R., Alvis-Guzman N., Amoako Y., Artaman A., et al. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:1683–1691. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

