PI3K Inhibitors in Advanced Breast Cancer: The Past, The Present, New Challenges and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 35565291
- PMCID: PMC9103982
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14092161
PI3K Inhibitors in Advanced Breast Cancer: The Past, The Present, New Challenges and Future Perspectives
Abstract
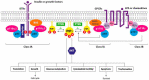
Breast cancer is the leading cause of death in the female population and despite significant efforts made in diagnostic approaches and treatment strategies adopted for advanced breast cancer, the disease still remains incurable. Therefore, development of more effective systemic treatments constitutes a crucial need. Recently, several clinical trials were performed to find innovative predictive biomarkers and to improve the outcome of metastatic breast cancer through innovative therapeutic algorithms. In the pathogenesis of breast cancer, the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-protein kinase B (PKB/AKT)-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) axis is a key regulator of cell proliferation, growth, survival, metabolism, and motility, making it an interest and therapeutic target. Nevertheless, the PI3K/AKT/mTOR cascade includes a complex network of biological events, needing more sophisticated approaches for their use in cancer treatment. In this review, we described the rationale for targeting the PI3K pathway, the development of PI3K inhibitors and the future treatment directions of different breast cancer subtypes in the metastatic setting.
Keywords: PI3K inhibitors; biomarkers; clinical trial; liquid biopsy; next-generation sequencing; precision medicine; real-time PCR; subtype breast cancer; target therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

