Prognostic Impact of EGFR Amplification and Visceral Pleural Invasion in Early Stage Pulmonary Squamous Cell Carcinomas Patients after Surgical Resection of Primary Tumor
- PMID: 35565304
- PMCID: PMC9101408
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14092174
Prognostic Impact of EGFR Amplification and Visceral Pleural Invasion in Early Stage Pulmonary Squamous Cell Carcinomas Patients after Surgical Resection of Primary Tumor
Abstract
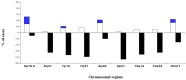
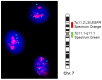
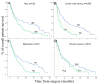
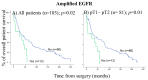
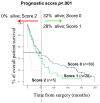
Over the last few decades, an increasing amount of information has been accumulated on biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Despite these advances, most biomarkers have been identified in the adenocarcinoma histological subtype (AC). However, the application of molecular-targeted therapies in the prognosis and treatment of SCC in the clinical setting is very limited, becoming one of the main focus areas in research. Here, we prospectively analyzed the frequency of numerical/structural abnormalities of chromosomes 5, 7, 8, 9, 13 and 22 with FISH in 48 pulmonary SCC patients. From a total of 12 probes, only abnormalities of the 7p12 and 22q12 chromosomal regions were identified as unique genetic variables associated with the prognosis of the disease. The study for these two chromosomal regions was extended to 108 patients with SCC. Overall, chromosome losses were observed more frequently than chromosome gains, i.e., 61% versus 19% of all the chromosome abnormalities detected. The highest levels of genetic amplification were detected for the 5p15.2, 7p12, 8q24 and 22q11 chromosome bands, of which several genes are potentially involved in the pathogenesis of SCC, among others, include the EGFR gene at chromosome 7p12. Patients who displayed EGFR amplification (n = 13; 12%) were mostly older than 65 years (p = 0.07) and exclusively patients in early T-primary tumor stage (pT1−pT2; p = 0.03) with a significantly shortened overall survival (OS) (p ≤ 0.001). Regarding prognosis, the clinical, biological, and histopathologic characteristics of the disease that displayed a significant adverse influence on OS in the univariate analysis included patients older than 65 years (p = 0.02), the presence of lymph node involvement (p = 0.005), metastasis (p = 0.01) and, visceral pleural invasion (VPI) at diagnosis (p = 0.04). EGFR amplification also conferred an adverse impact on patient OS in the whole series (p = 0.02) and especially in patients in early stages (pT1−pT2; p = 0.01). A multivariate analysis of the prognostic factors for OS showed that the most informative combination of independent variables to predict an adverse outcome was the presence of VPI and/or EGFR amplification (p < 0.001). Based on these two variables, a scoring system was built to stratify patients into low- (no adverse features: score 0; n = 69), intermediate- (one adverse feature: score 1; n = 29) and high-risk (two adverse features: score 2; n = 5) groups, with significantly different (p = 0.001) OS rates at 50 months, which were as following: 32%, 28% and 0%, respectively. In the present study, we show that the presence of a high level of 7p12 (EGFR) amplification, exclusively detected in early stage SCC (pT1−pT2), is an independent adverse prognostic factor for OS. The identification of the EGFR gene copy number using FISH techniques may provide a more accurate diagnosis of high-risk populations after the complete resection of the primary tumor. When combined with VPI, three groups of pulmonary SCC were clearly identified that show the extent of the disease. This is of such importance that further prospective studies are necessary in larger series of SCC patients to be classified at the time of diagnosis. This could be achieved with the combined assessment of 7p12 amplification and VPI in primary tumor samples.
Keywords: EGFR amplification; early stage; prognosis; squamous cell lung carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of visceral pleural invasion in the stage pT1-2N2M0 non-small cell lung cancer: A study based on the SEER registry.Curr Probl Cancer. 2021 Feb;45(1):100640. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2020.100640. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Curr Probl Cancer. 2021. PMID: 32828574
-
Visceral pleura invasion by non-small cell lung cancer: an underrated bad prognostic factor.Ann Thorac Surg. 2001 Apr;71(4):1088-93. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(00)02649-7. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001. PMID: 11308141
-
Gain of the EGFR gene located on 7p12 is a frequent and early event in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung.Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2008 Jul;184(1):31-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2008.03.002. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2008. PMID: 18558286
-
Clinicopathologic features and prognostic implications of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene copy number and protein expression in non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2006 Dec;54(3):387-98. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.08.015. Epub 2006 Sep 29. Lung Cancer. 2006. PMID: 17011067
-
Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-74039-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17993229 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk analysis of visceral pleural invasion in malignant solitary pulmonary nodules that appear touching the pleural surface.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2024 Jan-Dec;18:17534666241285606. doi: 10.1177/17534666241285606. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2024. PMID: 39380304 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Parameters and Extracellular Volume Fraction as Predictors of Lung Cancer Subtypes and Lymph Node Status in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients.J Cancer. 2023 Sep 25;14(16):3108-3116. doi: 10.7150/jca.88367. eCollection 2023. J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37859821 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the genetic variations associated with response to first-line chemotherapy in patients with small cell lung cancer: a retrospective cohort study.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Dec 30;15(12):7013-7023. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1772. Epub 2023 Dec 26. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 38249933 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially Expressed Genes Involved in Primary Resistance to Immunotherapy in Patients with Advanced-Stage Pulmonary Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 8;25(4):2048. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042048. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396726 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance and prognostic value of CT-defined visceral pleural invasion in early-stage lung adenocarcinomas.Eur Radiol. 2024 Mar;34(3):1934-1945. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10204-2. Epub 2023 Sep 2. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37658899
References
-
- Kris M.G., Johnson B.E., Kwiatkowski D.J., Iafrate A.J., Wistuba I.I., Aronson S.L., Shyr Y., Khuri F.R., Rudin C.M., Garon E.B., et al. Identification of driver mutations in tumor specimens from 1,000 patients with lung adenocarcinoma: The NCI’s Lung Cancer Mutation Consortium (LCMC) J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29((Suppl. 18)):CRA7506. doi: 10.1200/jco.2011.29.15_suppl.cra7506. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

