Cytokines: Can Cancer Get the Message?
- PMID: 35565306
- PMCID: PMC9103018
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14092178
Cytokines: Can Cancer Get the Message?
Abstract
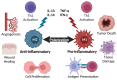
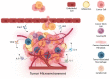
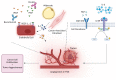
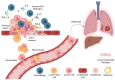
Cytokines are small molecular messengers that have profound effects on cancer development. Increasing evidence shows that cytokines are heavily involved in regulating both pro- and antitumor activities, such as immune activation and suppression, inflammation, cell damage, angiogenesis, cancer stem-cell-like cell maintenance, invasion, and metastasis. Cytokines are often required to drive these cancer-related processes and, therefore, represent an important research area for understanding cancer development and the potential identification of novel therapeutic targets. Interestingly, some cytokines are reported to be related to both pro- and anti-tumorigenicity, indicating that cytokines may play several complex roles relating to cancer pathogenesis. In this review, we discuss some major cancer-related processes and their relationship with several cytokines.
Keywords: angiogenesis; cytokines; inflammation; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Identification of a new pro-invasion factor in tumor microenvironment: progress in function and mechanism of extracellular ATP].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017 Apr 18;49(2):188-195. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017. PMID: 28416823 Chinese.
-
Identification and functional study of cytokines and chemokines involved in tumorigenesis.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2012 Mar;15(3):276-85. doi: 10.2174/138620712799218608. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2012. PMID: 22221060 Review.
-
The role of inflammation in head and neck cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;816:107-27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-0837-8_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24818721 Review.
-
Cytokine Regulation of Metastasis and Tumorigenicity.Adv Cancer Res. 2016;132:265-367. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Adv Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27613135 Review.
-
Inflammatory cytokines in bladder cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Sep;234(9):14489-14499. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28252. Epub 2019 Feb 18. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30779110 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress Linking Obesity and Cancer: Is Obesity a 'Radical Trigger' to Cancer?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 8;24(9):8452. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098452. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CXCL12 restricts tumor growth by suppressing the Ras, ERK1/2, c-Myc, and the immune checkpoint PD-L1 pathways.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Dec 24;121(52):e2416909121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2416909121. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39689179 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging Evolutionary Immunology in Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-17 Signaling for Lung Cancer Therapeutics.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Nov 22;7(12):3658-3670. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00412. eCollection 2024 Dec 13. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39698267 Review.
-
Tumor dormancy and relapse: understanding the molecular mechanisms of cancer recurrence.Mil Med Res. 2025 Feb 11;12(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40779-025-00595-2. Mil Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39934876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-33 (IL-33) promotes DNA damage-resistance in lung cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Apr 11;16(1):274. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07624-x. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40216748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New DimensionsHallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

