Transcriptomic Profiling of Gene Expression Associated with Granulosa Cell Tumor Development in a Mouse Model
- PMID: 35565312
- PMCID: PMC9105549
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14092184
Transcriptomic Profiling of Gene Expression Associated with Granulosa Cell Tumor Development in a Mouse Model
Abstract
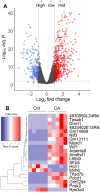
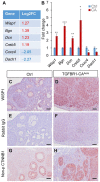
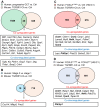
Ovarian granulosa cell tumors (GCTs) are rare sex cord-stromal tumors, accounting for ~5% ovarian tumors. The etiology of GCTs remains poorly defined. Genetically engineered mouse models are potentially valuable for understanding the pathogenesis of GCTs. Mice harboring constitutively active TGFβ signaling (TGFBR1-CA) develop ovarian GCTs that phenocopy several hormonal and molecular characteristics of human GCTs. To determine molecular alterations in the ovary upon TGFβ signaling activation, we performed transcriptomic profiling of gene expression associated with GCT development using ovaries from 1-month-old TGFBR1-CA mice and age-matched controls. RNA-sequencing and bioinformatics analysis coupled with the validation of select target genes revealed dysregulations of multiple cellular events and signaling molecules/pathways. The differentially expressed genes are enriched not only for known GCT-related pathways and tumorigenic events but also for signaling events potentially mediated by neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, relaxin signaling, insulin signaling, and complements in TGFBR1-CA ovaries. Additionally, a comparative analysis of our data in mice with genes dysregulated in human GCTs or granulosa cells overexpressing a mutant FOXL2, the genetic hallmark of adult GCTs, identified some common genes altered in both conditions. In summary, this study has revealed the molecular signature of ovarian GCTs in a mouse model that harbors the constitutive activation of TGFBR1. The findings may be further exploited to understand the pathogenesis of a class of poorly defined ovarian tumors.
Keywords: TGFBR1; gene ontology; granulosa cell tumors; signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pangas S.A., Li X., Umans L., Zwijsen A., Huylebroeck D., Gutierrez C., Wang D., Martin J.F., Jamin S.P., Behringer R.R., et al. Conditional deletion of smad1 and smad5 in somatic cells of male and female gonads leads to metastatic tumor development in mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008;28:248–257. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01404-07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Edson M.A., Nalam R.L., Clementi C., Franco H.L., Demayo F.J., Lyons K.M., Pangas S.A., Matzuk M.M. Granulosa cell-expressed bmpr1a and bmpr1b have unique functions in regulating fertility but act redundantly to suppress ovarian tumor development. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010;24:1251–1266. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0461. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

