Automatic Cancer Cell Taxonomy Using an Ensemble of Deep Neural Networks
- PMID: 35565352
- PMCID: PMC9100154
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14092224
Automatic Cancer Cell Taxonomy Using an Ensemble of Deep Neural Networks
Abstract
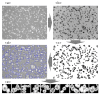
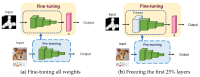
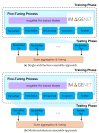
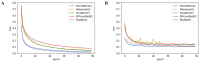
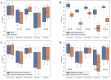
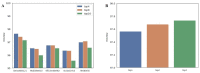
Microscopic image-based analysis has been intensively performed for pathological studies and diagnosis of diseases. However, mis-authentication of cell lines due to misjudgments by pathologists has been recognized as a serious problem. To address this problem, we propose a deep-learning-based approach for the automatic taxonomy of cancer cell types. A total of 889 bright-field microscopic images of four cancer cell lines were acquired using a benchtop microscope. Individual cells were further segmented and augmented to increase the image dataset. Afterward, deep transfer learning was adopted to accelerate the classification of cancer types. Experiments revealed that the deep-learning-based methods outperformed traditional machine-learning-based methods. Moreover, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test showed that deep ensemble approaches outperformed individual deep-learning-based models (p < 0.001) and were in effect to achieve the classification accuracy up to 97.735%. Additional investigation with the Wilcoxon signed-rank test was conducted to consider various network design choices, such as the type of optimizer, type of learning rate scheduler, degree of fine-tuning, and use of data augmentation. Finally, it was found that the using data augmentation and updating all the weights of a network during fine-tuning improve the overall performance of individual convolutional neural network models.
Keywords: cancer cell taxonomy; convolutional neural network; deep learning; ensemble approach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A novel end-to-end classifier using domain transferred deep convolutional neural networks for biomedical images.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2017 Mar;140:283-293. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.12.019. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2017. PMID: 28254085
-
Skin lesion classification with ensembles of deep convolutional neural networks.J Biomed Inform. 2018 Oct;86:25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2018.08.006. Epub 2018 Aug 10. J Biomed Inform. 2018. PMID: 30103029
-
Recognition of peripheral blood cell images using convolutional neural networks.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019 Oct;180:105020. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105020. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019. PMID: 31425939
-
Advances Towards Automatic Detection and Classification of Parasites Microscopic Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network: Methods, Models and Research Directions.Arch Comput Methods Eng. 2023;30(3):2013-2039. doi: 10.1007/s11831-022-09858-w. Epub 2022 Dec 3. Arch Comput Methods Eng. 2023. PMID: 36531561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Survey of Deep Learning for Lung Disease Detection on Medical Images: State-of-the-Art, Taxonomy, Issues and Future Directions.J Imaging. 2020 Dec 1;6(12):131. doi: 10.3390/jimaging6120131. J Imaging. 2020. PMID: 34460528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Automated Recognition of Cancer Tissues through Deep Learning Framework from the Photoacoustic Specimen.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Aug 10;2022:4356744. doi: 10.1155/2022/4356744. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36017020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Position Paper on Mammography Screening. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2014. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- NRF-2019R1F1A1062397/National Research Foundation of Korea
- NRF-2021R1F1A1059665/National Research Foundation of Korea
- Dept. of IT Convergence Engineering, Kumoh National Institute of Technology/Brain Korea 21 FOUR Project
- Dept. of Data Science at Seoul National University of Science and Technology/Brain Korea 21 FOUR Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

