Worldwide Burden, Risk Factors, and Temporal Trends of Ovarian Cancer: A Global Study
- PMID: 35565359
- PMCID: PMC9102475
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14092230
Worldwide Burden, Risk Factors, and Temporal Trends of Ovarian Cancer: A Global Study
Abstract
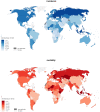
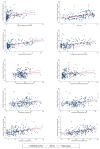
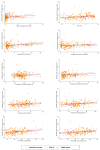
This study aimed to investigate the most updated worldwide incidence and mortality, risk factors, and epidemiologic trend of ovarian cancer in different countries, regions, and age groups. The Global Cancer Observatory database was used for incidence and mortality rates of ovarian cancer in 2020. Data from Cancer Incidence in Five Continents and the WHO mortality database was accessed for trend analysis. Age-standardized rates (ASRs, per 100,000 persons) were calculated for incidence and mortality. The 10-year annual average percent change (AAPC) was estimated by Joinpoint regression analysis. There was an overall decreasing trend of ovarian cancer, yet its burden has been increasing in lower-income countries and among younger females in some countries. Intensive lifestyle modifications are warranted, especially for the populations at high risk for ovarian cancer, including smoking cessation, alcohol use reduction, physical activity, weight control, and treatment of metabolic diseases.
Keywords: incidence; mortality; ovarian cancer; risk factors; temporal trends.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

