Compassionate Use Program of Ipilimumab and Nivolumab in Intermediate or Poor Risk Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Large Multicenter Italian Study
- PMID: 35565422
- PMCID: PMC9105283
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14092293
Compassionate Use Program of Ipilimumab and Nivolumab in Intermediate or Poor Risk Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Large Multicenter Italian Study
Abstract
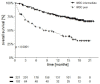
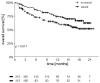
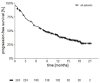
This is a retrospective analysis on the safety and activity of compassionate Ipilimumab and Nivolumab (IPI-NIVO) administered to patients with metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (mRCC) with intermediate or poor International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium (IMDC) score as a first-line regimen. IPI was infused at 1 mg/kg in combination with Nivolumab 3 mg/kg every three weeks for four doses, followed by maintenance Nivolumab (240 or 480 mg flat dose every two or four weeks, respectively) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. A total of 324 patients started IPI-NIVO at 86 Italian centers. Median age was 62 years, 68.2% IMDC intermediate risk. Primary tumor had been removed in 65.1% of patients. Two hundred and twenty patients (67.9%) completed the four IPI-NIVO doses. Investigator-assessed overall response rate was 37.6% (2.8% complete). Twelve-month survival rate was 66.8%, median progression-free survival was 8.3 months. Grade 3 or 4 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 67 patients (26.9%). IMDC intermediate risk, nephrectomy, BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2, and steroid use for toxicities correlated with improved survival, while age < 70 years did not. IPI-NIVO combination is a feasible and effective regimen for the first-line treatment of intermediate-poor IMDC risk mRCC patients in routine clinical practice.
Keywords: immune-related adverse events; ipilimumab; metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma; nivolumab; progression; retrospective; survival; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
UB: advisory board for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Speaker’s fees and travel grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Ipsen; FP: none; MR: none; UDG: received honoraria for advisory boards or invited speaker fees from Pfizer, BMS, MSD, PharmaMar, Astellas, Bayer, Ipsen, Novartis, Roche, Clovis, AstraZeneca, institutional research grants from AstraZeneca, Sanofi and Roche; SB: advisory board or steering committee member for Astellas, Janssen, Pfizer, MSD, BMS, IPSEN, Roche, AAA, Bayer, Sanofi-Genzyme, Merck, AstraZeneca, LA: none, FA: none; GC: none; GP: none; LF: none, MDA: none, GF: none; PZ: reports outside the submitted work personal fees for advisory role, speaker engagements, and travel and accommodation expenses from MSD, Astellas, Janssen, Sanofi, Ipsen, Pfizer, Novartis, Bristol Meyer Squibb, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Roche, and Bayer; AC: none, MS: none, SP: none, CC: none; SP: none; FMD: none; VZ: advisory role for Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, EISAI and Italfarmaco, speakers’ bureau for Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Astellas, Servier, Astra Zeneca, MSD, Janssen, Ipsen, research funding from Bayer, Roche, Lilly, Astra Zeneca, BMS, Ipsen, Astellas, travel grants from Bayer, Roche, Servier; GT: none.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in previously untreated advanced renal-cell carcinoma: analysis of Japanese patients in CheckMate 214 with extended follow-up.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jan 24;50(1):12-19. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyz132. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31633185 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab and Ipilimumab for Advanced or Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study.Curr Oncol. 2021 Apr 3;28(2):1402-1411. doi: 10.3390/curroncol28020133. Curr Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33916792 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of nivolumab plus ipilimumab with tyrosine kinase inhibitors as first-line therapies for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: a multicenter retrospective study.Int J Clin Oncol. 2021 Jan;26(1):154-162. doi: 10.1007/s10147-020-01797-5. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Int J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33067647
-
[Immunotherapy for renal cell carcinoma - current status].Aktuelle Urol. 2018 Apr;49(2):187-191. doi: 10.1055/a-0581-4451. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Aktuelle Urol. 2018. PMID: 29587324 Review. German.
-
Risks and benefits of reinduction ipilimumab/nivolumab in melanoma patients previously treated with ipilimumab/nivolumab.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Oct;9(10):e003395. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003395. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34702752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Real-world efficacy and safety of nivolumab and ipilimumab in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a Polish multicenter study.Future Oncol. 2025 Jun;21(15):1895-1904. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2508138. Epub 2025 May 20. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40391586
-
Impact of pretreatment body mass index on clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving first-line immune checkpoint inhibitor-based therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Investig Clin Urol. 2024 Sep;65(5):423-434. doi: 10.4111/icu.20240052. Investig Clin Urol. 2024. PMID: 39249914 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of nivolumab and ipilimumab in older adults with renal cell carcinoma: findings from a multicenter observational study in Poland.Front Oncol. 2025 Aug 19;15:1617743. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1617743. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40904494 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Meet-URO score in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving first-line nivolumab and ipilimumab in the Italian Expanded Access Program.ESMO Open. 2022 Dec;7(6):100634. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100634. Epub 2022 Dec 6. ESMO Open. 2022. PMID: 36493602 Free PMC article.
-
The Effectiveness and Safety Profile of Nivolumab-Plus-Ipilimumab in Previously Untreated Japanese Patients With Advanced or Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (J-ENCORE Study).Int J Urol. 2025 Aug;32(8):961-972. doi: 10.1111/iju.70076. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Int J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40271863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cella D., Grünwald V., Nathan P., Doan J., Dastani H., Taylor F., Bennett B., DeRosa M., Berry S., Broglio K., et al. Quality of life in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma given nivolumab versus everolimus in CheckMate 025: A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:994–1003. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30125-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hammers H.J., Plimack E.R., Infante J.R., Rini B.I., McDermott D.F., Lewis L.D., Voss M.H., Sharma P., Pal S.K., Razak A.R.A., et al. Safety and efficacy of nivolumab in combination with ipilimumab in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: The CheckMate 016 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017;35:3851–3858. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.72.1985. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Motzer R.J., Tannir N.M., McDermott D.F., Arén Frontera O., Melichar B., Choueiri T.K., Plimack E.R., Barthélémy P., Porta C., George S., et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018;378:1277–1290. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1712126. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

