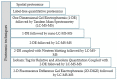
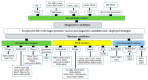
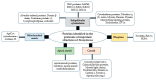
Mining the Proteome of Toxoplasma Parasites Seeking Vaccine and Diagnostic Candidates
- PMID: 35565525
- PMCID: PMC9099775
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12091098
Mining the Proteome of Toxoplasma Parasites Seeking Vaccine and Diagnostic Candidates
Abstract
Toxoplasma gondii is a pathogenic protozoan parasite that infects the nucleated cells of warm-blooded hosts leading to an infectious zoonotic disease known as toxoplasmosis. The infection outcomes might be severe and fatal in patients with immunodeficiency, diabetes, and pregnant women and infants. The One Health approach to toxoplasmosis highlights that the health of humans is closely related to the health of animals and our common environment. The presence of drug resistance and side effects, the further improvement of sensitivity and specificity of serodiagnostic tools and the potentiality of vaccine candidates to induce the host immune response are considered as justifiable reasons for the identification of novel targets for the better management of toxoplasmosis. Thus, the identification of new critical proteins in the proteome of Toxoplasma parasites can also be helpful in designing and test more effective drugs, vaccines, and diagnostic tools. Accordingly, in this study we present important proteins found in the proteome of the life cycle-specific stages of Toxoplasma parasites that are potential diagnostic or vaccine candidates. The current study might help to understand the complexity of these parasites and provide a possible source of strategies and biomolecules that can be further evaluated in the pathobiology of Toxoplasma parasites and for diagnostics and vaccine trials against this disease.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii; diagnostics; targets; toxoplasmosis; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Host cell proteins modulated upon Toxoplasma infection identified using proteomic approaches: a molecular rationale.Parasitol Res. 2022 Jul;121(7):1853-1865. doi: 10.1007/s00436-022-07541-4. Epub 2022 May 13. Parasitol Res. 2022. PMID: 35552534 Review.
-
Vaccination as a control strategy against the coccidial parasites Eimeria, Toxoplasma and Neospora.Parasitology. 2006;133 Suppl:S145-68. doi: 10.1017/S0031182006001855. Parasitology. 2006. PMID: 17274844 Review.
-
Macrophage Stimulation as a Useful Approach for Immunoscreening of Potential Vaccine Candidates Against Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum Infections.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2411:129-144. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1888-2_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34816403
-
Key Limitations and New Insights Into the Toxoplasma gondii Parasite Stage Switching for Future Vaccine Development in Human, Livestock, and Cats.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Nov 25;10:607198. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.607198. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33324583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Toxoplasma gondii vaccine encoding multistage antigens in conjunction with ubiquitin confers protective immunity to BALB/c mice against parasite infection.Parasit Vectors. 2015 Sep 30;8:498. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-1108-7. Parasit Vectors. 2015. PMID: 26420606 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Proteomics Applications in Toxoplasma gondii: Unveiling the Host-Parasite Interactions and Therapeutic Target Discovery.Pathogens. 2023 Dec 29;13(1):33. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13010033. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 38251340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research on inner membrane complex protein 1: a novel nanovaccines against Toxoplasma gondii.BMC Vet Res. 2025 Aug 23;21(1):521. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04961-z. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40849645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dubey J.P. Toxoplasma gondii. 3rd ed. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020. The history and life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii; pp. 1–19.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources