The Effects of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb, Anemone chinensis Bunge, and Smilax glabra Roxb on Broiler Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, and Gastrointestinal Tract Microorganisms
- PMID: 35565537
- PMCID: PMC9105906
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12091110
The Effects of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb, Anemone chinensis Bunge, and Smilax glabra Roxb on Broiler Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, and Gastrointestinal Tract Microorganisms
Abstract
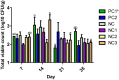
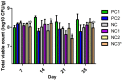
Poultry farming is growing globally, particularly in developing countries, to meet the demands of growing populations for poultry meat and eggs. This is likely to lead to an increase in the use of antibiotics in poultry feed, thus contributing to the development and spread of antibiotic resistance which, poses a serious threat to human and animal health worldwide. One way of reducing this threat is to reduce the use of antibiotics in poultry production by finding effective and sustainable antibiotic alternatives that can be used to support poultry health and productivity. Therefore, this study evaluates the incorporation of three medicinal plants, Anemone chinensis Bunge, Smilax glabra Roxb, and Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb, in poultry feed on production performance, nutrient digestibility, and bacteria in the chicken caecum in a 35-day performance trial with 420-day-old male Ross 308 broilers. Groups of randomly selected chicks received one of six dietary treatments. These included five experimental diets of reduced nutrient specifications as a negative control (NC); with amoxicillin as a positive antibiotic control (PC1); with A. pilosa Ledeb (NC1); with A. chinensis Bunge (NC2); and with S. glabra Roxb (NC3). One other positive control diet contained the recommended nutrient specification (PC2). Weight gain and feed intake were measured weekly and used to calculate the feed conversion ratio as performance parameters. Bacteria were enumerated from chicken caecum using a traditional plating method and selective agar. S. glabra Roxb and A. chinensis Bunge showed comparable effects to amoxicillin with significantly increased weight gain in birds offered these diets, compared to those offered the negative control from days 0 to 35 (p < 0.001). S. glabra Roxb exhibited effects similar to the amoxicillin control group with an improved feed conversion ratio (p < 0.001). In addition, S. glabra Roxb decreased numbers of E. coli and Campylobacter spp. on days 21 (p < 0.05) and 35 (p < 0.01) and increased numbers of lactic acid bacteria comparable to the antibiotic group on days 14 (p < 0.001) and 35 (p < 0.01). The findings of this in vivo trial highlight the potential of S. glabra Roxb and A. chinensis Bunge as beneficial feed material to promote poultry health and productivity in the absence of antibiotics.
Keywords: Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb; Anemone chinensis Bunge; and Smilax glabra Roxb; broiler chickens; lactic acid bacteria; performance; plants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal’s guidelines and declare no conflicts of interest. Co-authors CD and JT are employees of Devenish Nutrition and they contributed to the ammonia measurements. Devenish Nutrition has no competing interests and did not provide funding for the trial. The funder (DAERA) had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibacterial Activity of Four Plant Extracts Extracted from Traditional Chinese Medicinal Plants against Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli, and Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis.Microorganisms. 2020 Jun 26;8(6):962. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8060962. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32604894 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of endo-1,4-beta-xylanase supplementation to low-energy diets on performance, blood constituents, nutrient digestibility, and gene expressions related growth of broiler chickens.J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2024 Jan;108(1):99-110. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13870. Epub 2023 Aug 16. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2024. PMID: 37587735
-
Evaluating a novel consensus bacterial 6-phytase variant on growth performance of broilers fed U.S. commercial diets deficient in nutrients and energy through 63 days of age.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skac407. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac407. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 36516414 Free PMC article.
-
A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Dietary Yeast Mannan-Rich Fraction on Broiler Performance and the Implication for Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Chicken Production.Animals (Basel). 2024 May 28;14(11):1595. doi: 10.3390/ani14111595. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organic Acids and Potential for Modifying the Avian Gastrointestinal Tract and Reducing Pathogens and Disease.Front Vet Sci. 2018 Sep 6;5:216. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00216. eCollection 2018. Front Vet Sci. 2018. PMID: 30238011 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Screen of Traditional Chinese Medicinal Plant Extracts Reveals 17 Species with Antimicrobial Properties.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Dec 17;13(12):1220. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13121220. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mottet A., Tempio G. Global poultry production: Current state and future outlook and challenges. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2017;73:245–256. doi: 10.1017/S0043933917000071. - DOI
-
- Alexandratos N., Bruinsma J. World agriculture towards 2030/2050. Food Agric. Organ. U. N. 2012:1–147. doi: 10.22004/ag.econ.288998. - DOI
-
- OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2020–2029. [(accessed on 4 April 2022)]. Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/agriculture-and-food/oecd-fao-agricultural....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

