Horse Racing as a Model to Study the Relationship between Air Pollutants and Physical Performance
- PMID: 35565565
- PMCID: PMC9103629
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12091139
Horse Racing as a Model to Study the Relationship between Air Pollutants and Physical Performance
Abstract
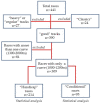
This study proposes the theoretical principles for the selection of a sample of horse races to study the relationship between air pollutants and performance. These criteria were then applied to an original dataset comparing the correlations between these variables obtained in "Handicap" versus "Conditional" type races.
Methods: The mean concentration of pollutants during the six hours prior to the race and the speed of the test were determined in 441 official races at a racecourse in Santiago, Chile, during the summer and winter months of 2012. Using layout, track condition and distance (1000, 1100 and 1200 m) as criteria, a homogeneous group of races ("Handicap"; n = 214) versus a heterogeneous group ("Conditional"; n = 95) were compared using simple correlations (Spearman's test).
Results: Race speed was related to greater levels of PM10, PM2.5, NO2, NO and SO2 and it was positively related to O3, a trend that was observed in the 1000, 1100 m races and in the total "Handicap" group. Similar results were observed only in 1000 m for the "Conditional" group with lower Rho, except for PM10 and PM2.5. The total races of the conditional group showed lower Rho values and significant associations of the same trend for CO, NO2, NO and SO2.
Conclusions: Horse races between 1000 and 1200 m of the "Handicap" type appear to be an interesting group to study the relationship between air pollutants and the performance of racehorses. In the future, our observations should be expanded to other distances and other types of races.
Keywords: air pollution; exercise; performance; thoroughbred racehorses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Atmospheric Pollutants Affect Physical Performance: A Natural Experiment in Horse Racing Studied by Principal Component Analysis.Biology (Basel). 2022 Apr 30;11(5):687. doi: 10.3390/biology11050687. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35625415 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of racing performance in the Japanese Thoroughbred horse:: II. Environmental variation of racing time on turf and dirt tracks and the influence of sex, age, and weight carried on racing time.J Anim Breed Genet. 1994 Jan 12;111(1-6):128-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0388.1994.tb00446.x. J Anim Breed Genet. 1994. PMID: 21395760
-
Effects of short-term exposure to air pollution on hospital admissions of young children for acute lower respiratory infections in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2012 Jun;(169):5-72; discussion 73-83. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2012. PMID: 22849236
-
Association between exposure to ambient air pollution and hospital admission, incidence, and mortality of stroke: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of more than 23 million participants.Environ Health Prev Med. 2021 Jan 26;26(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12199-021-00937-1. Environ Health Prev Med. 2021. PMID: 33499804 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term exposure to particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3) and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Environ Int. 2020 Sep;142:105876. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105876. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Environ Int. 2020. PMID: 32590284
Cited by
-
Exposure to chemical pollutants and biological aerosol in indoor facilities for recreational and sport horses.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Feb 28;20(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-03930-2. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38413934 Free PMC article.
-
How equestrians conceptualise horse welfare: Does it facilitate or hinder change?Anim Welf. 2023 Sep 1;32:e59. doi: 10.1017/awf.2023.79. eCollection 2023. Anim Welf. 2023. PMID: 38487466 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of ambient air pollution exposure on Thoroughbred racehorse performance.Equine Vet J. 2025 May;57(3):712-722. doi: 10.1111/evj.14415. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Equine Vet J. 2025. PMID: 39228107 Free PMC article.
-
Atmospheric Pollutants Affect Physical Performance: A Natural Experiment in Horse Racing Studied by Principal Component Analysis.Biology (Basel). 2022 Apr 30;11(5):687. doi: 10.3390/biology11050687. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35625415 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

