The Transcription Regulator YgeK Affects Biofilm Formation and Environmental Stress Resistance in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 35565586
- PMCID: PMC9100123
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12091160
The Transcription Regulator YgeK Affects Biofilm Formation and Environmental Stress Resistance in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
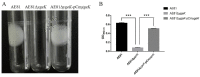
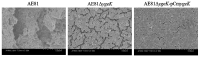
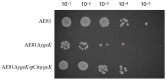
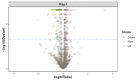
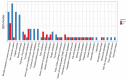
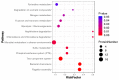
Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) is one of the most common pathogens in poultry and a potential gene source of human extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC), leading to serious economic losses in the poultry industry and public health concerns. Exploring the pathogenic mechanisms underpinning APEC and the identification of new targets for disease prevention and treatment are warranted. YgeK is a transcriptional regulator in APEC and is localized to the type III secretion system 2 of E. coli. In our previous work, the transcription factor ygeK significantly affected APEC flagella formation, bacterial motility, serum sensitivity, adhesion, and virulence. To further explore ygeK functions, we evaluated its influence on APEC biofilm formation and resistance to environmental stress. Our results showed that ygeK inactivation decreased biofilm formation and reduced bacterial resistance to environmental stresses, including acid and oxidative stress. In addition, the multi-level regulation of ygeK in APEC was analyzed using proteomics, and associations between differentially expressed proteins and the key targets of ygeK were investigated. Overall, we identified ygeK's new function in APEC. These have led us to better understand the transcriptional regulatory ygeK and provide new clues about the pathogenicity of APEC.
Keywords: avian pathogenic Escherichia coli; biofilm; environmental stress; transcription regulators; ygeK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
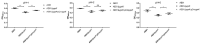
Similar articles
-
Characteristics, pathogenic mechanism, zoonotic potential, drug resistance, and prevention of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC).Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 13;13:1049391. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1049391. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36583051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription Regulator YgeK Affects the Virulence of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli.Animals (Basel). 2021 Oct 20;11(11):3018. doi: 10.3390/ani11113018. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827751 Free PMC article.
-
LuxR family transcriptional repressor YjjQ modulates the biofilm formation and motility of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli.Res Vet Sci. 2022 Dec 20;152:10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2022.07.011. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Res Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35901637
-
The ETT2 transcriptional regulator EivF affects the serum resistance and pathogenicity of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli.Microb Pathog. 2021 Dec;161(Pt A):105261. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105261. Epub 2021 Oct 25. Microb Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34710562
-
Identification of novel biofilm genes in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli by Tn5 transposon mutant library.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jun 11;38(8):130. doi: 10.1007/s11274-022-03314-4. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35688968 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic distribution, characterization, and function of Escherichia coli type III secretion system 2 (ETT2).iScience. 2024 Apr 18;27(5):109763. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109763. eCollection 2024 May 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38706860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics, pathogenic mechanism, zoonotic potential, drug resistance, and prevention of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC).Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 13;13:1049391. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1049391. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36583051 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

