Novel Quantitative PCR for Rhodococcus equi and Macrolide Resistance Detection in Equine Respiratory Samples
- PMID: 35565598
- PMCID: PMC9099730
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12091172
Novel Quantitative PCR for Rhodococcus equi and Macrolide Resistance Detection in Equine Respiratory Samples
Abstract
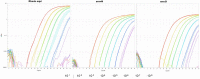
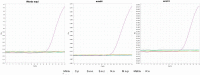
R. equi is an important veterinary pathogen that takes the lives of many foals every year. With the emergence and spread of MDR R. equi to current antimicrobial treatment, new tools that can provide a fast and accurate diagnosis of the disease and antimicrobial resistance profile are needed. Here, we have developed and analytically validated a multiplex qPCR for the simultaneous detection of R. equi and related macrolide resistance genes in equine respiratory samples. The three sets of oligos designed in this study to identify R. equi housekeeping gene choE and macrolide resistance genes erm(46) and erm(51) showed high analytic sensitivity with a limit of detection (LOD) individually and in combination below 12 complete genome copies per PCR reaction, and an amplification efficiency between 90% and 147%. Additionally, our multiplex qPCR shows high specificity in in-silico analysis. Furthermore, it did not present any cross-reaction with normal flora from the equine respiratory tract, nor commonly encountered respiratory pathogens in horses or other genetically close organisms. Our new quantitative PCR is a trustable tool that will improve the speed of R. equi infection diagnosis, as well as helping in treatment selection.
Keywords: Rhodococcus equi; diagnosis; erm(46); erm(51); macrolide resistance; qPCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clonal Confinement of a Highly Mobile Resistance Element Driven by Combination Therapy in Rhodococcus equi.mBio. 2019 Oct 15;10(5):e02260-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02260-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31615959 Free PMC article.
-
Novel transferable erm(46) determinant responsible for emerging macrolide resistance in Rhodococcus equi.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015 Dec;70(12):3184-90. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkv279. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26377866
-
Antimicrobial resistance among Streptococcus equi subspecies zooepidemicus and Rhodococcus equi isolated from equine specimens submitted to a diagnostic laboratory in Kentucky, USA.PeerJ. 2022 Sep 21;10:e13682. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13682. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36164606 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodococcus Equi: Challenges to Treat Infections and to Mitigate Antimicrobial Resistance.J Equine Vet Sci. 2023 Aug;127:104845. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2023.104845. Epub 2023 Jun 7. J Equine Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37295760 Review.
-
Epidemiology and Molecular Basis of Multidrug Resistance in Rhodococcus equi.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2021 Apr 14;85(2):e00011-21. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00011-21. Print 2021 May 19. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33853933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rhodococcus equi, an Unusual Human Pathogen That Causes Cavitating Pneumonia in Patients With AIDS.Case Rep Infect Dis. 2024 Nov 7;2024:5570186. doi: 10.1155/2024/5570186. eCollection 2024. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39545099 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-host distribution of Rhodococcus equi (Prescottella equi) strains and their phylogenomic clustering.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Jul 21;25(1):447. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-04152-8. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40691552 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

