Breast Milk Iodine Concentration (BMIC) as a Biomarker of Iodine Status in Lactating Women and Children <2 Years of Age: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35565659
- PMCID: PMC9104537
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14091691
Breast Milk Iodine Concentration (BMIC) as a Biomarker of Iodine Status in Lactating Women and Children <2 Years of Age: A Systematic Review
Abstract
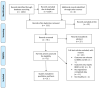
Background: Iodine is needed for the production of thyroid hormones, which are essential for infant growth and development. Given that there are wide variations in breast milk iodine concentration (BMIC) and urinary iodine concentration (UIC), it is unclear if BMIC is associated with UIC in populations residing in iodine sufficient or deficient areas. Aim: To investigate if BMIC can be used as a biomarker for iodine status in lactating women and children <2 years of age. Methods: Electronic databases; PubMed, Web of Science and Scopus were searched until year 2021, for studies investigating the relationship between BMIC and UIC. Studies were reviewed for eligibility, according to inclusion and exclusion criteria, followed by data extraction, according to the PRISMA guidelines. Results: Overall, 51 studies met the criteria for inclusion in the systematic review. BMIC ranged from 18 to 1153 µg/L. In iodine-deficient and iodine-sufficient lactating women, BMIC ranged from 26 to 185 µg/L and 15 to 1006 µg/L, respectively. In most studies, the categorisation of iodine status assessed by median UIC was consistent with the categorisation of iodine status assessed by median BMIC cut off of ≥100 µg/L, to determine iodine sufficiency in lactating women and children <2 years of age. Conclusions: The systematic review indicated that BMIC is a promising biomarker of iodine status in lactating women and children <2 years of age. However, these data need to be interpreted cautiously, given the study limitations in the included studies. Future studies should consider investigating the optimal median BMIC, as there is a lack of high-quality observational and intervention studies in lactating women and infants.
Keywords: breast milk; breast milk iodine concentration; infant; lactation; maternal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Iodine nutrition status in lactating mothers residing in countries with mandatory and voluntary iodine fortification programs: an updated systematic review.Thyroid. 2015 Jun;25(6):611-20. doi: 10.1089/thy.2014.0491. Epub 2015 May 14. Thyroid. 2015. PMID: 25811835
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(26):1-149. doi: 10.3310/hta5260. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701099
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Folate supplementation in people with sickle cell disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 16;3(3):CD011130. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011130.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29546732 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Iodine Status of Infants and Toddlers under 2 Years of Age and Its Association with Feeding Behaviors and Maternal Iodine Status in Shanghai: A Quantile Regression Analysis.Nutrients. 2024 May 29;16(11):1686. doi: 10.3390/nu16111686. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892618 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the Elemental Iodine in Human Breast Milk by Inductively Coupled Plasma mass Spectrometry.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 Apr;202(4):1517-1523. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03786-x. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 37500822
-
Biomarkers of Micronutrients and Phytonutrients and Their Application in Epidemiological Studies.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 15;15(4):970. doi: 10.3390/nu15040970. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36839326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Iodine Concentration in Human Milk from Donors: Implications for Preterm Infants.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 14;14(20):4304. doi: 10.3390/nu14204304. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36296988 Free PMC article.
-
Low Iodine Nutrition Knowledge in Chinese Breastfeeding Women despite Adequate Iodine Status.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 8;16(4):491. doi: 10.3390/nu16040491. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38398815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Assessment of Iodine Deficiency Disorders And monitoring Their Elimination: A Guide for Programme Managers. World Health Organization (WHO); Geneva, Switzerland: 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous