Myristica fragrans Extract Regulates Gut Microbes and Metabolites to Attenuate Hepatic Inflammation and Lipid Metabolism Disorders via the AhR-FAS and NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Mice with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- PMID: 35565666
- PMCID: PMC9104743
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14091699
Myristica fragrans Extract Regulates Gut Microbes and Metabolites to Attenuate Hepatic Inflammation and Lipid Metabolism Disorders via the AhR-FAS and NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Mice with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
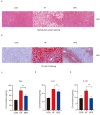
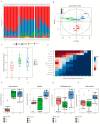
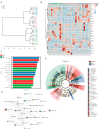
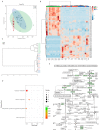
Recent studies have shown that non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is closely related to the gut microbiome. Myristica fragrans is widely used as a traditional seasoning and has a therapeutic effect on gastrointestinal diseases. Although previous studies have shown that M. fragrans extracts have anti-obesity and anti-diabetes effects in mice fed a high-fat diet, few studies have determined the active components or the corresponding mechanism in vivo. In this study, for the first time, an M. fragrans extract (MFE) was shown to be a prebiotic that regulates gut microbes and metabolites in mice fed a high-fat diet. Bioinformatics, network pharmacology, microbiome, and metabolomics analyses were used to analyze the nutrient-target pathway interactions in mice with NAFLD. The National Center for Biotechnology Information Gene Expression Omnibus database was used to analyze NAFLD-related clinical data sets to predict potential targets. The drug database and disease database were then integrated to perform microbiome and metabolomics analyses to predict the target pathways. The concentrations of inflammatory factors in the serum and liver, such as interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α, were downregulated by MFE. We also found that the hepatic concentrations of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglycerides were decreased after MFE treatment. Inhibition of the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway and downregulation of the fatty acid synthase (FAS)-sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c pathway resulted in the regulation of inflammation and lipid metabolism by activating tryptophan metabolite-mediated aryl hydrocarbon receptors (AhR). In summary, MFE effectively attenuated inflammation and lipid metabolism disorders in mice with NAFLD through the NF-κB and AhR-FAS pathways.
Keywords: Myristica fragrans extract; aryl hydrocarbon receptor; gut microbes; metabolites; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; nuclear factor kappa B.
Conflict of interest statement
This work has not been published previously and the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
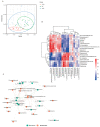
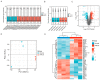
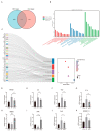
References
-
- Borrelli A., Bonelli P., Tuccillo F.M., Goldfine I.D., Evans J.L., Buonaguro F.M., Mancini A. Role of gut microbiota and oxidative stress in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease to hepatocarcinoma: Current and innovative therapeutic approaches. Redox Biol. 2018;15:467–479. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.01.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rahman K., Desai C., Iyer S.S., Thorn N.E., Kumar P., Liu Y., Smith T., Neish A.S., Li H., Tan S. Loss of Junctional Adhesion Molecule A Promotes Severe Steatohepatitis in Mice on a Diet High in Saturated Fat, Fructose, and Cholesterol-ScienceDirect. Gastroenterology. 2016;151:733–746. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.06.022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

