Effect of L-Glutamine on Chylomicron Formation and Fat-Induced Activation of Intestinal Mucosal Mast Cells in Sprague-Dawley Rats
- PMID: 35565745
- PMCID: PMC9104139
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14091777
Effect of L-Glutamine on Chylomicron Formation and Fat-Induced Activation of Intestinal Mucosal Mast Cells in Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
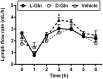
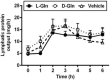
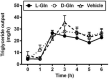
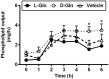
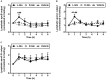
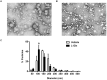
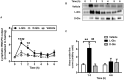
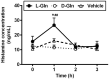
Glutamine (Gln) is required for intestinal mucosal homeostasis, and it can promote triglyceride absorption. The intestinal mucosal mast cells (MMCs) are activated during fat absorption. This study investigated the potential role of Gln on fat absorption-induced activation of MMCs in rats. Lymph fistula rats (n = 24) were studied after an overnight recovery with the infusion of saline only, saline plus 85 mM L-glutamine (L-Gln) or 85 mM D-glutamine (D-Gln), respectively. On the test day, rats (n = 8/group) were given an intraduodenal bolus of 20% Intralipid contained either saline only (vehicle group), 85 mM L-Gln (L-Gln group), or 85 mM D-Gln (D-Gln group). Lymph was collected hourly for up to 6 h for analyses. The results showed that intestinal lymph from rats given L-Gln had increased levels of apolipoprotein B (ApoB) and A-I (ApoA-I), concomitant with an increased spectrum of smaller chylomicron particles. Unexpectedly, L-Gln also increased levels of rat mucosal mast cell protease II (RMCPII), as well as histamine and prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) in response to dietary lipid. However, these effects were not observed in rats treated with 85 mM of the stereoisomer D-Gln. Our results showed that L-glutamine could specifically activate MMCs to degranulate and release MMC mediators to the lymph during fat absorption. This observation is potentially important clinically since L-glutamine is often used to promote gut health and repair leaky gut.
Keywords: L-glutamine; apolipoproteins; intestinal lymph; intestinal mucosal mast cell; lipid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibiotics Suppress Activation of Intestinal Mucosal Mast Cells and Reduce Dietary Lipid Absorption in Sprague-Dawley Rats.Gastroenterology. 2016 Nov;151(5):923-932. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.07.009. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 27436071 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of rat intestinal mucosal mast cells by fat absorption.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Jun 1;302(11):G1292-300. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00011.2012. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22461027 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine promotes triglyceride absorption in a dose-dependent manner.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002 Feb;282(2):G317-23. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.2002.282.2.G317. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11804853
-
The Role of Interstitial Matrix and the Lymphatic System in Gastrointestinal Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism.Front Physiol. 2020 Jan 22;11:4. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00004. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32038309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutrient-induced inflammation in the intestine.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011 Jul;14(4):315-21. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283476e74. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011. PMID: 21587069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Innate immunity in pancreatic cancer: Lineage tracing and function.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 16;13:1081919. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1081919. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36726981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Dietary Components on Mast Cells: Possible Use as Nutraceuticals for Allergies?Cells. 2023 Nov 10;12(22):2602. doi: 10.3390/cells12222602. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37998337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutamine Peptides: Preparation, Analysis, Applications, and Their Role in Intestinal Barrier Protection.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 14;17(6):1017. doi: 10.3390/nu17061017. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40290078 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

