Olfactory Stimulation with Volatile Aroma Compounds of Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) Essential Oil and Linalool Ameliorates White Fat Accumulation and Dyslipidemia in Chronically Stressed Rats
- PMID: 35565791
- PMCID: PMC9105046
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14091822
Olfactory Stimulation with Volatile Aroma Compounds of Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) Essential Oil and Linalool Ameliorates White Fat Accumulation and Dyslipidemia in Chronically Stressed Rats
Abstract
We explored the physiological effects of inhaling basil essential oil (BEO) and/or linalool and identified odor-active aroma compounds in BEO using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and GC-olfactometry (GC-O). Linalool was identified as the major volatile compound in BEO. Three groups of rats were administered BEO and linalool via inhalation, while rats in the control group were not. Inhalation of BEO for 20 min only reduced the total weight gain (190.67 ± 2.52 g) and increased the forced swimming time (47.33 ± 14.84 s) compared with the control group (219.67 ± 2.08 g, 8.33 ± 5.13 s). Inhalation of BEO for 5 min (392 ± 21 beats/min) only reduced the pulse compared with the control group (420 ± 19 beats/min). Inhalation of linalool only reduced the weight of white adipose tissue (5.75 ± 0.61 g). The levels of stress-related hormones were not significantly different among the groups. The total cholesterol and triglyceride levels decreased after inhalation of BEO for 20 min (by more than -10% and -15%, respectively). Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels were lowered (by more than -10%) by the inhalation of BEO and linalool, regardless of the inhalation time. In particular, BEO inhalation for 20 min was associated with the lowest level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (53.94 ± 2.72 mg/dL). High-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels increased after inhalation of BEO (by more than +15%). The atherogenic index and cardiac risk factors were suppressed by BEO inhalation. Animals exposed to BEO and linalool had no significant differences in hepatotoxicity. These data suggest that the inhalation of BEO and linalool may ameliorate cardiovascular and lipid dysfunctions. These effects should be explored further for clinical applications.
Keywords: Ocimum basilicum L.; essential oil; linalool; stress lipid metabolism; volatile compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
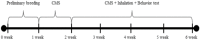
Similar articles
-
Inhalation of low-dose basil (Ocimum basilicum) essential oil improved cardiovascular health and plasma lipid markers in high fat diet-induced obese rats.J Food Sci. 2022 Jun;87(6):2450-2462. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16196. Epub 2022 May 19. J Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 35591766
-
α-Linalool - a marker compound of forged/synthetic sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) essential oils.J Sci Food Agric. 2013 Oct;93(13):3292-303. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6175. Epub 2013 May 15. J Sci Food Agric. 2013. PMID: 23584979
-
Acaricidal and anthelmintic efficacy of Ocimum basilicum essential oil and its major constituents estragole and linalool, with insights on acetylcholinesterase inhibition.Vet Parasitol. 2022 Sep;309:109743. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2022.109743. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Vet Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35714433
-
Intraplantar injection of bergamot essential oil into the mouse hindpaw: effects on capsaicin-induced nociceptive behaviors.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009;85:237-48. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(09)85018-6. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19607974 Review.
-
Relationship between mood change, odour and its physiological effects in humans while inhaling the fragrances of essential oils as well as linalool and its enantiomers.Molecules. 2013 Mar 13;18(3):3312-38. doi: 10.3390/molecules18033312. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 23486108 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nootkatone (NK), a grapefruit-derived aromatic compound, inhibited lipid accumulation by regulating JAK2-STAT signaling and antioxidant response in adipocyte.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Feb 3;33(11):2631-2641. doi: 10.1007/s10068-024-01522-2. eCollection 2024 Aug. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39144189 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of inhalation application of lavender essential oil on slaughter and carcass characteristics and serum biochemistry in Texas quail.Poult Sci. 2025 Jun;104(6):104828. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104828. Epub 2025 Mar 29. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40222346 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Properties of Natural Products and Human Health.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 29;15(13):2961. doi: 10.3390/nu15132961. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Piskunov A., Stepanichev M., Tishkina A., Novikova M., Levshina I., Gulyaeva N. Chronic combined stress induces selective and long-lasting inflammatory response evoked by changes in corticosterone accumulation and signaling in rat hippocampus. Metab. Brain Dis. 2016;31:445–454. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9785-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

