Oral Supplement Containing Hydroxytyrosol and Punicalagin Improves Dyslipidemia in an Adult Population without Co-Adjuvant Treatment: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled and Crossover Trial
- PMID: 35565844
- PMCID: PMC9103949
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14091879
Oral Supplement Containing Hydroxytyrosol and Punicalagin Improves Dyslipidemia in an Adult Population without Co-Adjuvant Treatment: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled and Crossover Trial
Abstract
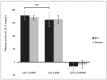
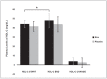
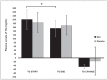
Hydroxytyrosol (HT) and punicalagin (PC) exert cardioprotective and antiatherosclerotic effects. This study evaluated the effect of an oral supplement containing HT and PC (SAx) on dyslipidemia in an adult population. A randomized, double-blind, controlled, crossover trial was conducted over a 20-week period. SAx significantly reduced the plasma levels of triglycerides (TG) in subjects with hypertriglyceridemia (≥150 mg/dL) (from 200.67 ± 51.38 to 155.33 ± 42.44 mg/dL; p < 0.05), while no such effects were observed in these subjects after the placebo. SAx also significantly decreased the plasma levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in subjects with high plasma levels of LDL-C (≥160 mg/dL) (from 179.13 ± 16.18 to 162.93 ± 27.05 mg/dL; p < 0.01), while no such positive effect was observed with the placebo. In addition, the placebo significantly reduced the plasma levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in the total population (from 64.49 ± 12.65 to 62.55 ± 11.57 mg/dL; p < 0.05), while SAx significantly increased the plasma levels of HDL-C in subjects with low plasma levels of HDL-C (<50 mg/dL) (from 44.25 ± 3.99 to 48.00 ± 7.27 mg/dL; p < 0.05). In conclusion, the supplement containing HT and PC exerted antiatherosclerotic and cardio-protective effects by considerably improving dyslipidemia in an adult population, without co-adjuvant treatment or adverse effects.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cardiovascular disease; dyslipidemia; high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; hydroxytyrosol; low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; punicalagin; total cholesterol; triglycerides.
Conflict of interest statement
A.Z. is employed by Euromed S.A. but had no role in the design, collection and/or analysis of the data.
Figures
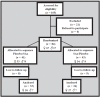
References
-
- WHO Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) [(accessed on 19 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases...
-
- Kaptoge S., Pennells L., De Bacquer D., Cooney M.T., Kavousi M., Stevens G., Riley L.M., Savin S., Khan T., Altay S., et al. World Health Organization cardiovascular disease risk charts: Revised models to estimate risk in 21 global regions. Lancet Glob. Health. 2019;7:e1332–e1345. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30318-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) [(accessed on 7 September 2016)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/
-
- WHO . Global Atlas on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Control. The World Health Organization Press in Collaboration with the World Heart Federation and the World Stroke Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

