Glycomacropeptide Safety and Its Effect on Gut Microbiota in Patients with Phenylketonuria: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 35565850
- PMCID: PMC9104775
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14091883
Glycomacropeptide Safety and Its Effect on Gut Microbiota in Patients with Phenylketonuria: A Pilot Study
Abstract
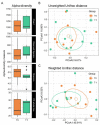
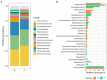
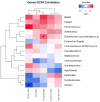
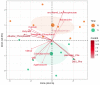
Glycomacropeptide (GMP) represents a good alternative protein source in Phenylketonuria (PKU). In a mouse model, it has been suggested to exert a prebiotic role on beneficial gut bacteria. In this study, we performed the 16S rRNA sequencing to evaluate the effect of 6 months of GMP supplementation on the gut microbiota of nine PKU patients, comparing their bacterial composition and clinical parameters before and after the intervention. GMP seems to be safe from both the microbiological and the clinical point of view. Indeed, we did not observe dramatic changes in the gut microbiota but a specific prebiotic effect on the butyrate-producer Agathobacter spp. and, to a lesser extent, of Subdoligranulum. Clinically, GMP intake did not show a significant impact on both metabolic control, as phenylalanine values were kept below the age target and nutritional parameters. On the other hand, an amelioration of calcium phosphate homeostasis was observed, with an increase in plasmatic vitamin D and a decrease in alkaline phosphatase. Our results suggest GMP as a safe alternative in the PKU diet and its possible prebiotic role on specific taxa without causing dramatic changes in the commensal microbiota.
Keywords: Agathobacter; GMP; Subdoligranulum; calcium homeostasis; diet; glycomacropeptide; gut microbiota; nutritional therapy; phenylketonuria; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycomacropeptide is a prebiotic that reduces Desulfovibrio bacteria, increases cecal short-chain fatty acids, and is anti-inflammatory in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Oct 1;309(7):G590-601. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00211.2015. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26251473 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic changes demonstrate reduced bioavailability of tyrosine and altered metabolism of tryptophan via the kynurenine pathway with ingestion of medical foods in phenylketonuria.Mol Genet Metab. 2017 Jun;121(2):96-103. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2017.04.003. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Mol Genet Metab. 2017. PMID: 28400091 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phenylketonuria Diet Promotes Shifts in Firmicutes Populations.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Apr 16;9:101. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00101. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31058098 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Glycomacropeptide in Patients with Phenylketonuria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2018 Nov 18;10(11):1794. doi: 10.3390/nu10111794. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30453665 Free PMC article.
-
Glycomacropeptide-Based Protein Substitutes for Children with Phenylketonuria in Italy: A Nutritional Comparison.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 27;16(7):956. doi: 10.3390/nu16070956. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38612990 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Bovine Kappa-Casein Glycomacropeptide in Modulating the Microbiome and Inflammatory Responses of Irritable Bowel Syndrome.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 15;15(18):3991. doi: 10.3390/nu15183991. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the Potential of Casein Glycomacropeptide in Adult Irritable Bowel Syndrome Management: A Pilot Study.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 27;15(19):4174. doi: 10.3390/nu15194174. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37836457 Free PMC article.
-
Milk Bioactive Compounds and Gut Microbiota Modulation: The Role of Whey Proteins and Milk Oligosaccharides.Foods. 2024 Mar 16;13(6):907. doi: 10.3390/foods13060907. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38540897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Berberine alleviates enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced intestinal mucosal barrier function damage in a piglet model by modulation of the intestinal microbiome.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 14;11:1494348. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1494348. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39877539 Free PMC article.
-
Morphofunctional Assessment beyond Malnutrition: Fat Mass Assessment in Adult Patients with Phenylketonuria-Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 11;16(12):1833. doi: 10.3390/nu16121833. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38931188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Spronsen F.J., van Wegberg A.M., Ahring K., Bélanger-Quintana A., Blau N., Bosch A.M., Burlina A., Campistol J., Feillet F., Giżewska M., et al. Key European Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Patients with Phenylketonuria. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:743–756. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(16)30320-5. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

