Sleep Quality: A Narrative Review on Nutrition, Stimulants, and Physical Activity as Important Factors
- PMID: 35565879
- PMCID: PMC9103473
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14091912
Sleep Quality: A Narrative Review on Nutrition, Stimulants, and Physical Activity as Important Factors
Abstract
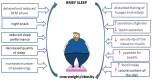
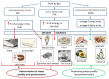
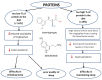
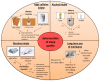
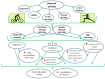
Sleep is a cyclically occurring, transient, and functional state that is controlled primarily by neurobiological processes. Sleep disorders and insomnia are increasingly being diagnosed at all ages. These are risk factors for depression, mental disorders, coronary heart disease, metabolic syndrome, and/or high blood pressure. A number of factors can negatively affect sleep quality, including the use of stimulants, stress, anxiety, and the use of electronic devices before sleep. A growing body of evidence suggests that nutrition, physical activity, and sleep hygiene can significantly affect the quality of sleep. The aim of this review was to discuss the factors that can affect sleep quality, such as nutrition, stimulants, and physical activity.
Keywords: nutrition; physical activity; sleep; stimulants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Saidi O., Rochette E., Doré É., Maso F., Raoux J., Andrieux F., Fantini M.L., Merlin E., Pereira B., Walrand S., et al. Randomized double-blind controlled trial on the effect of proteins with different tryptophan/large neutral amino acid ratios on sleep in adolescents: The protmorpheus study. Nutrients. 2020;12:1885. doi: 10.3390/nu12061885. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murawski B., Plotnikoff R.C., Rayward A.T., Vandelanotte C., Brown W.J., Duncan M.J. Randomised controlled trial using a theory-based m-health intervention to improve physical activity and sleep health in adults: The Synergy Study protocol. BMJ Open. 2018;8:e018997. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018997. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dashti H.S., Jones S.E., Wood A.R., Lane J.M., van Hees V.T., Wang H., Rhodes J.A., Song Y., Patel K., Anderson S.G., et al. Genome-wide association study identifies genetic loci for self-reported habitual sleep duration supported by accelerometer-derived estimates. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:1100. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08917-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

