Effects of Energy Drink Acute Assumption in Gastrointestinal Tract of Rats
- PMID: 35565895
- PMCID: PMC9105126
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14091928
Effects of Energy Drink Acute Assumption in Gastrointestinal Tract of Rats
Abstract
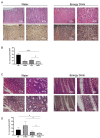
Energy drinks (EDs) are non-alcoholic beverages containing high amounts of caffeine and other psychoactive substances. EDs also contain herbal extract whose concentration is usually unknown. EDs can have several adverse effects on different organs and systems, but their effects on the gastrointestinal (GI) tract have been poorly investigated. To determine the acute effects of EDs on the GI tract, we administered EDs, coffee, soda cola, or water to Sprague-Dawley rats (n = 7 per group, randomly assigned) for up to five days, and analyzed the histopathological changes in the GI tract. Data were compared among groups by Kruskal-Wallis or Mann-Whitney tests. We found that, while EDs did not cause any evident acute lesion to the GI tract, they triggered eosinophilic infiltration in the intestinal mucosa; treatment with caffeine alone at the same doses found in EDs leads to the same effects, suggesting that it is caffeine and not other substances present in the EDs that causes this infiltration. The interruption of caffeine administration leads to the complete resolution of eosinophilic infiltration. As no systemic changes in pro-inflammatory or immunomodulating molecules were observed, our data suggest that caffeine present in ED can cause a local, transient inflammatory status that recruits eosinophils.
Keywords: caffeine; energy drinks; eosinophils.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
School pupils and university students surveyed for drinking beverages containing caffeine.Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2014;65(2):113-7. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig. 2014. PMID: 25272577
-
Caffeinated energy drink consumption among adolescents and potential health consequences associated with their use: a significant public health hazard.Acta Biomed. 2017 Aug 23;88(2):222-231. doi: 10.23750/abm.v88i2.6664. Acta Biomed. 2017. PMID: 28845841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Energy drink consumption and impact on caffeine risk.Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2014;31(9):1476-88. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2014.940608. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2014. PMID: 25010189
-
The metabolic disorders associated with chronic consumption of soft and energy drinks in rats.Acta Biochim Pol. 2020 Mar 19;67(1):79-84. doi: 10.18388/abp.2020_2914. Acta Biochim Pol. 2020. PMID: 32191411
-
Methodological and metabolic considerations in the study of caffeine-containing energy drinks.Nutr Rev. 2014 Oct;72 Suppl 1:137-45. doi: 10.1111/nure.12131. Nutr Rev. 2014. PMID: 25293552 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of the Severity and the Remission Criteria in Eosinophilic Esophagitis.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 1;11(12):3204. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123204. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Pancreatitis Pain Associated With Energy Drink Consumption: A Case Report.J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2024 Jan-Dec;12:23247096241255806. doi: 10.1177/23247096241255806. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38779965 Free PMC article.
-
The Dark Side of Energy Drinks: A Comprehensive Review of Their Impact on the Human Body.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 9;15(18):3922. doi: 10.3390/nu15183922. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Energy Drinks and Heart Damage in Young People.J Tehran Heart Cent. 2022 Oct;17(4):255-256. doi: 10.18502/jthc.v17i4.11617. J Tehran Heart Cent. 2022. PMID: 37143749 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evaluation of the Effects of Instant Cascara Beverage on the Brain-Gut Axis of Healthy Male and Female Rats.Nutrients. 2023 Dec 25;16(1):65. doi: 10.3390/nu16010065. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38201895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mattioli A.V., Pennella S., Manenti A., Ballerini Puviani M., Farinetti A. Influence of energy drinks on obesity: A preliminary experimental study. Prog. Nutr. 2018;19:369–372. doi: 10.23751/pn.v19i4.6438. - DOI
-
- Valle M.T.C., Couto-Pereira N.S., Lampert C., Arcego D.M., Toniazzo A.P., Limberger R.P., Dallegrave E., Dalmaz C., Arbo M.D., Leal M.B. Energy drinks and their component modulate attention, memory, and antioxidant defences in rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018;57:2501–2511. doi: 10.1007/s00394-017-1522-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Levy S., Santini L., Capucci A., Oto A., Santomauro M., Riganti C., Raviele A., Cappato R. European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society Statement on the cardiovascular events associated with the use or abuse of energy drinks. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. Int. J. Arrhythm. Pacing. 2019;56:99–115. doi: 10.1007/s10840-019-00610-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

