The Side-Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Increased BMI z-Score in Children with Overweight and Obesity in a Personalised Lifestyle Intervention One Year after the Start of the Pandemic in The Netherlands
- PMID: 35565909
- PMCID: PMC9104018
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14091942
The Side-Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Increased BMI z-Score in Children with Overweight and Obesity in a Personalised Lifestyle Intervention One Year after the Start of the Pandemic in The Netherlands
Abstract
Background: Early research showed weight gain in children during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Objective: To compare changes in BMI z-score of children with overweight and obesity in a personalised lifestyle intervention before and during the pandemic.
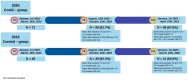
Methods: Changes in BMI z-score half a year (T6) and twelve months (T12) after the first lockdown were included for 71 children in the '2020 during COVID' group and compared to 48 children in the '2019 before COVID' group, using a marginal model for repeated measures (model 1). Model 2 corrected for lifestyle intervention characteristics, and model 3 corrected additionally for family characteristics.
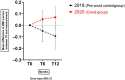
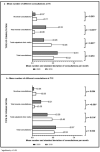
Results: The mean difference in BMI z-score change was significantly different at T12 (+0.07 in 2020 versus -0.09 in 2019, p = 0.022). Model 3 showed significant differences in BMI z-score change at both T6 (+0.15, p = 0.024) and T12 (+0.18, p = 0.016). This model also defined 'having a mother with obesity' (+0.13, p = 0.019) and the frequency of no-show consultations (+0.41 per missed consultation per month, p = 0.025) as related factors.
Conclusions: Lifestyle intervention in children with overweight and obesity is less successful in decreasing BMI z-score during the COVID-pandemic. Identified risk factors for less success could contribute to identifying children with higher risks for, and possibly prevent, BMI z-score increase.
Keywords: BMI; COVID-19; childhood obesity; obesity; overweight; pandemic; personalised lifestyle intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Weight Gain in Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Protective Effect of Lifestyle Intervention in Children with Obesity.Obes Facts. 2022;15(4):600-608. doi: 10.1159/000525298. Epub 2022 May 31. Obes Facts. 2022. PMID: 35640561 Free PMC article.
-
Nationwide Trends of Pediatric Obesity and BMI z-Score From 2017-2021 in China: Comparable Findings From Real-World Mobile- and Hospital-Based Data.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 26;13:859245. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.859245. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35721754 Free PMC article.
-
Sedentary Time and Fast-Food Consumption Associated With Weight Gain During COVID-19 Lockdown in Children and Adolescents With Overweight or Obesity.J Korean Med Sci. 2022 Mar 28;37(12):e103. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e103. J Korean Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35347907 Free PMC article.
-
Offspring body size and metabolic profile - effects of lifestyle intervention in obese pregnant women.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4893. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123127 Review.
-
Multicomponent Lifestyle Interventions for Treating Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses.J Obes. 2017;2017:5021902. doi: 10.1155/2017/5021902. Epub 2017 Dec 17. J Obes. 2017. PMID: 29391949 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessing the Impact of COVID-19 Prevention Measures on Adolescent Growth in Italy.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jul 24;11(14):2101. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11142101. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510542 Free PMC article.
-
Telemedicine Quality Improvement during the Corona Virus 2019 Pandemic Increases Pediatric Weight Management Access.Pediatr Qual Saf. 2024 May 9;9(3):e731. doi: 10.1097/pq9.0000000000000731. eCollection 2024 May-Jun. Pediatr Qual Saf. 2024. PMID: 38751895 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and Anthropometric Outcomes in Paediatric Patients with Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia after COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdowns: An Exploratory Analysis.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 8;16(13):2170. doi: 10.3390/nu16132170. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38999917 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Nutrition on Chronic Conditions.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 21;15(5):1066. doi: 10.3390/nu15051066. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36904066 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on obesity and it is risk factors: a systematic review.BMC Public Health. 2023 May 30;23(1):1018. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15833-2. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37254139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coronavirus Measures in Brief. Coronavirus COVID-19. Government.nl Ministerie van Algemene Zaken. [(accessed on 16 December 2021)]; Published 20 July 2020. Available online: https://www.government.nl/topics/c/coronavirus-covid-19/tackling-new-cor....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

